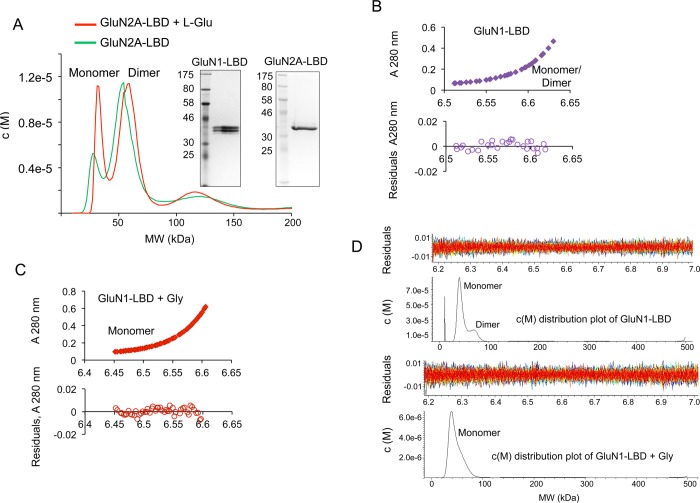
Figure 1.
Self-association of LBDs is disrupted by agonist binding. (A) c(M) distribution overlay after sedimentation velocity analysis of a primarily dimeric sample of GluN2A to highlight the increase in monomer population in the presence of l-Glu. Inset, SDS-PAGE showing purified protein preparations of GluN1-LBD and GluN2A-LBD respectively. (B) Sedimentation equilibrium analysis of GluN1 analyzed using SEDPHAT and fitted with the Species Analysis model for a combination of corresponding GluN1 monomeric and dimeric molecular weights. The bottom panel shows the residuals of the fitted data. (C) Sedimentation equilibrium data of GluN1 + 400 μM Gly were analyzed with SEDPHAT and fitted for GluN1 monomer size using the Species Analysis model. (D) Sedimentation velocity analysis of the GluN1-LBD analyzed using SEDFIT and showing c(M) distribution of molecular masses corresponding to monomeric and dimeric species in the presence or absence of Gly.