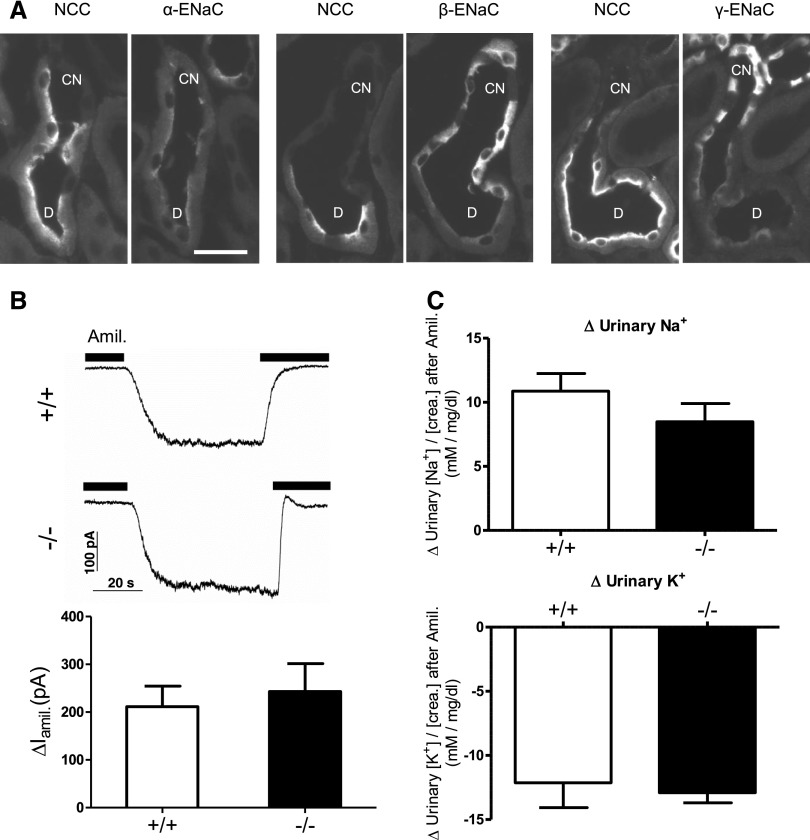
Figure 4.
Subcellular distribution and electrophysiologic activity of ENaC and amiloride response in kidneys of AS+/+ and AS−/− mice kept on a 2% K+ diet for 48 hours. (A) Detection of α-ENaC, β-ENaC, and γ-ENaC subunits and NCC in the late DCT (D) and CNT of AS-deficient (AS−/−) mice by immunofluorescence on kidney cryosections. Pairs of consecutive cryosections stained either for NCC or for one of the ENaC subunits are always shown. Tubules are identified by costaining for calbindin D28K (not shown) as described in the Concise Methods. (B) Amiloride-sensitive whole-cell currents (∆Iami) reflecting ENaC activity are measured by patch-clamp recordings on isolated early ASDN segments (DCT2/CNT) from AS+/+ and AS−/− mice kept on a 2% K+ diet for 48 hours. Representative whole-cell current traces are shown for AS−/− and AS+/+ mice. Currents are recorded using a pipette holding potential of −60 mV. Amiloride (Amil; 2 μM) is present as indicated by the black bars above the traces. The bar diagram summarizes results from similar experiments. n=7–9 measurements per group. (C) Difference (Δ) in urine [Na+]/[creatinine] and urine [K+]/[creatinine] ratios between vehicle (0.9% saline) and amiloride-injected mice. Amiloride or vehicle is injected intraperitoneally 48 hours after starting the feeding experiment. Urine is collected for the following 4 hours. n=8–11 mice per group. Values are the mean±SEM. Bar, approximately 25 μm.