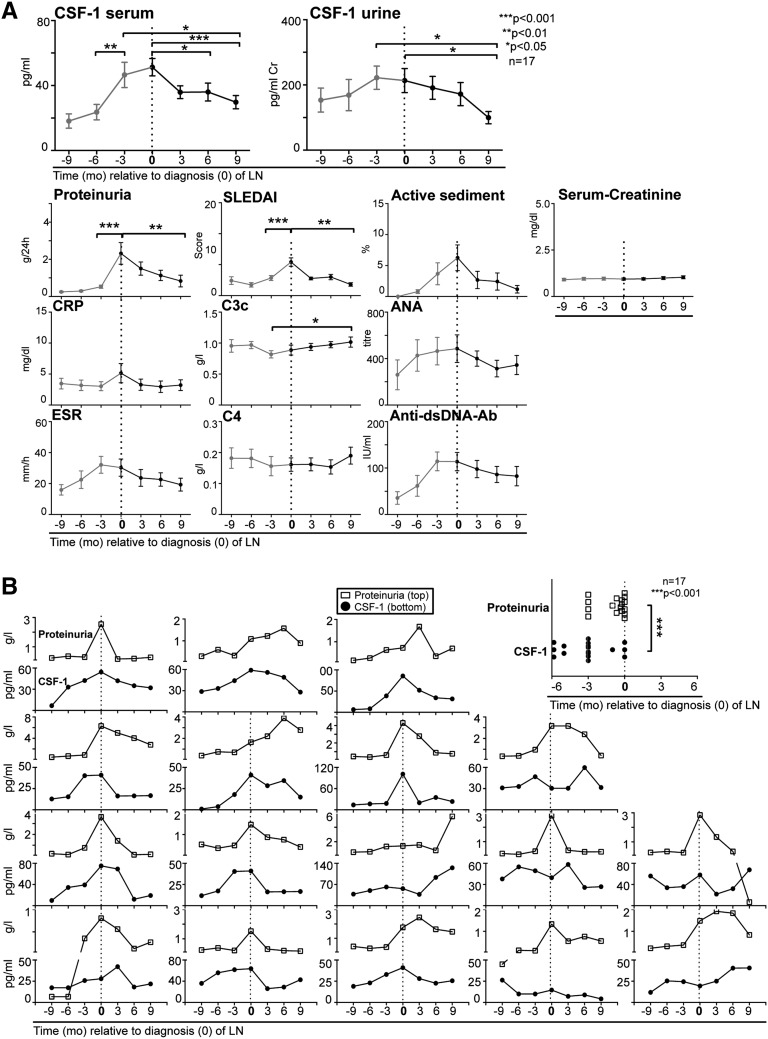
Figure 5.
Elevated serum and urine CSF-1 are a prognostic indicator of LN. (A) Composite patient values. Longitudinal tracked serum and urine CSF-1 levels in patients with SLE before (red) and at diagnosis of LN (time of renal biopsy, indicated as 0 time point) and at follow-up visits compared with conventional clinical indices of LN. Most patients had active LN without other lupus manifestation symptoms. Arthralgia, malar rash, and mild cutaneous manifestations were seen in <25% of the evaluated patients with LN. CSF-1 was quantified using ELISA. (B) Individual patient values. Left panel: Display of CSF-1 and proteinuria in each individual longitudinally tracked patient before, at, and after renal biopsy. Right panel: Comparison of elevated CSF-1 (defined as 50% higher than baseline) versus proteinuria (defined as urinary protein levels of ≥500 mg/24 hours) at each point before the patient’s renal biopsy. Before new-onset LN, the rise in CSF-1 levels (93±15 days) preceded an increase in proteinuria (27±9 days). Values are means±SEM. CRP, C-reactive protein.