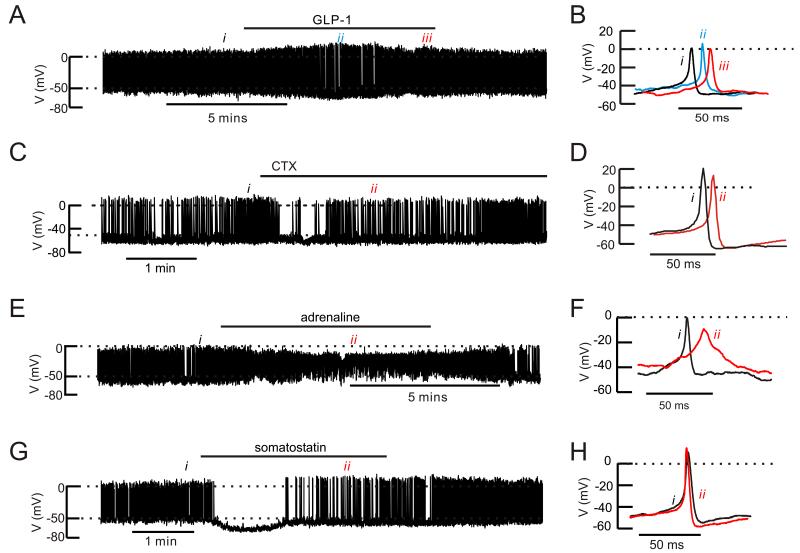
Figure 6.
Effects of GLP-1, ω-conotoxin, adrenaline and somatostatin on mouse α-cell electrical activity
(A) Action potential firing in an α-cell in an intact mouse islet at 1 mM glucose before, during and after addition of 10 nM GLP-1 (horizontal line).
(B) Examples of action potentials taken under control conditions (i), during the transient repolarization (ii) and at “steady-state” at the end of the GLP-1 application (iii).
(C) As in A but testing the effects of 100 nM ω-conotoxin on an isolated α-cell.
(D) Examples of action potentials recorded before (i) and after addition of ω-conotoxin (ii).
(E) As in A but 5 μM adrenaline was applied.
(F) Examples of action potentials under control conditions (i) and broad action potentials seen in the presence of adrenaline (ii)
(G) As in A but testing the effects of 100 nM somatostatin.
(H) Action potential recorded under control conditions (i) and when electrical activity had resumed in the continued presence of somatostatin (ii)
In A,C, E and F, the dotted horizontal lines indicate zero mV (top) and −50 mV (lower).