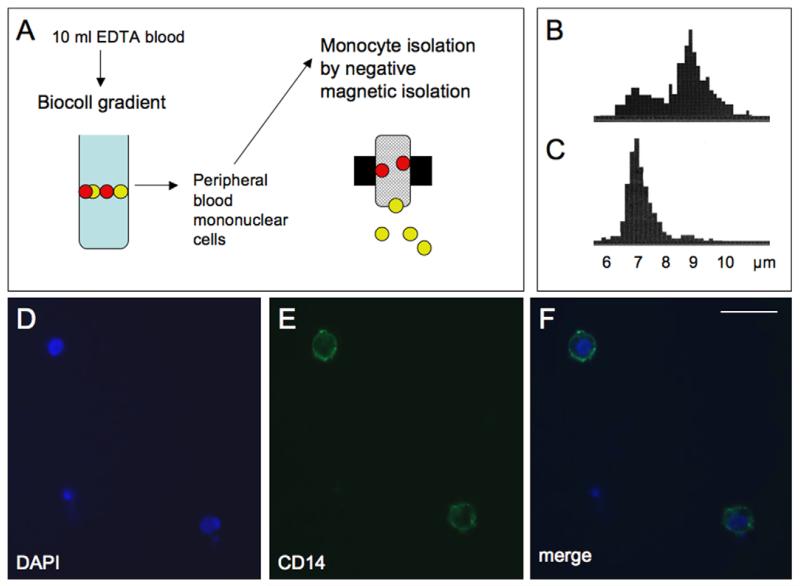
Fig. 1.
Isolation and immunohistochemical characterization of human monocytes. Monocytes were isolated by negative magnetic isolation (MACS) from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMS), which were collected from 10 ml EDTA blood after separation on a Biocoll gradient (A). PBMC counts displayed a double peak at approx. 7 and 9 μm (B), while after selective MACS isolation a single monocyte specific peak was visible at approx. 7 μm (C). Immunohistochemical staining of monocytes revealed intense CD14 immunoreactive cells (E), with DAPI positive nuclei (D), displaying that the majority of the isolated cells were monocytes (merge, F). Scale bar = 15 μm.