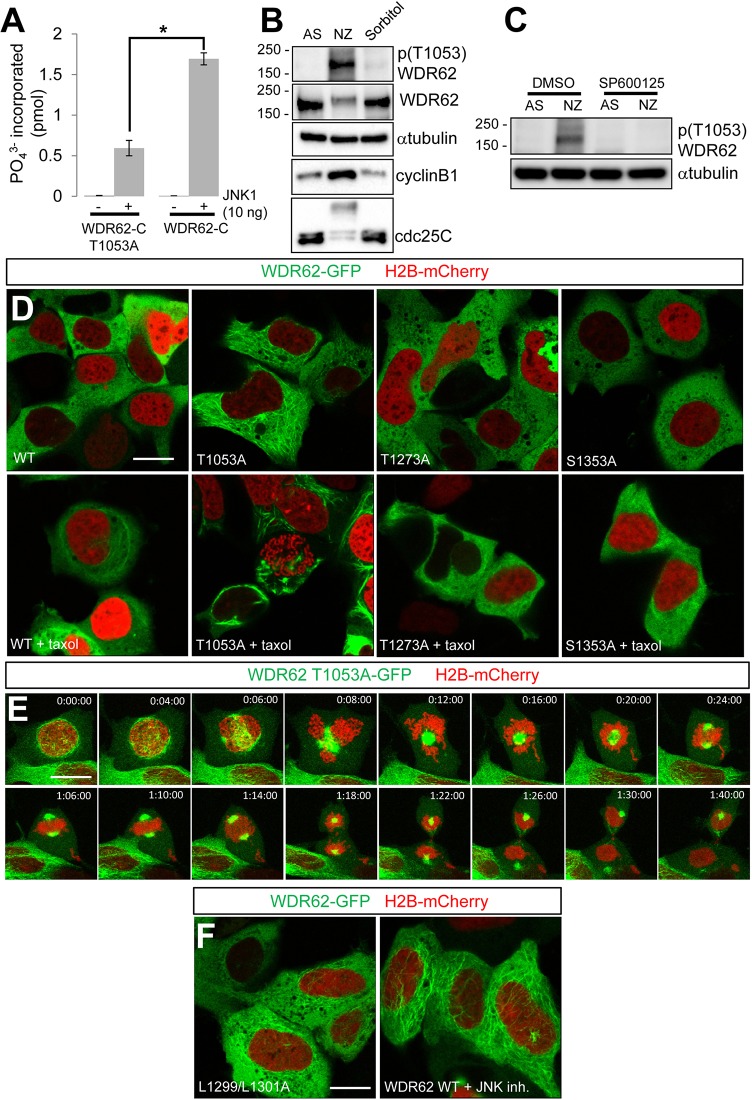
Fig. 3.
JNK-mediated phosphorylation of WDR62 maintains cytoplasmic localization during interphase. (A) In vitro phosphorylation of recombinantly expressed WDR62-C T1053A or WDR62-C by JNK1. Data show phosphate incorporation (pmol) and are expressed as the mean±s.e.m. (n = 3); *P<0.05 (Student's t-test). (B) AD293 cells were synchronized in mitosis (NZ, 350 nM, 16 h), stimulated with hyperosmotic stress (Sorbitol, 0.5 M, 30 min) or left untreated in asynchrony (AS), and the lysates were blotted as indicated. (C) JNK inhibition (SP600125, 20 µM, 60 min) decreased WDR62 T1053 phosphorylation in mitotic cells (NZ, 350 nM, 16 h). (D) The localization of GFP-tagged alanine-substituted WDR62 mutants (T1053A, T1273A, S1353A) or wild-type (WT) WDR62, coexpressed with mCherry-tagged H2B, was evaluated in non-dividing AD293 cells. The increased association of the WDR62 T1053A mutant with microtubules (compared to that of WDR62 T1273A or S1353A) was more evident following taxol-treatment (10 µM, 30 min). (E) Mitotic progression and division of a single AD293 cell expressing the GFP-tagged WDR62 T1053A mutant and H2B–mCherry. (F) Cytoplasmic microtubule association of the GFP-tagged JNK-binding-domain mutant of WDR62 (L1299/1301A) or wild-type WDR62 treated with JNK inhibitor [JNK inhibitor VIII (JNK inh.), 20 µM, 60 min]. Scale bars: 20 µm.