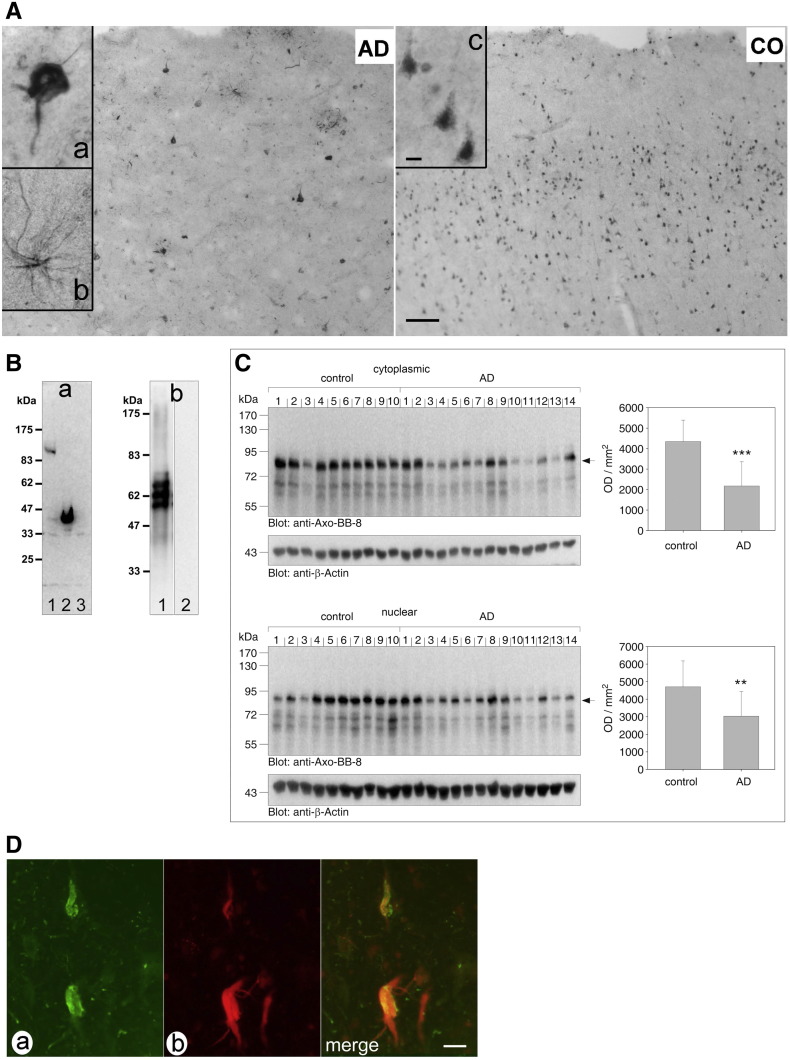
Fig. 4.
Axotrophin immunohistochemistry of human brain tissue. (A) Brain sections (area 22) were labeled with the affinity-purified anti-AxoCT antibody and visualized with DAB/Nickel. In control brain (CO, lower panel, scale bar: 100 μm) axotrophin is enriched in the nucleus of pyramidal cells in layer III and layer V and to a lesser extent in the cytoplasm and proximal dendrites of pyramidal cells (inset c, scale bar: 10 μm). In AD brain (AD upper panel, Braak stage V) the preferential nuclear localization is lost and axotrophin immunoreactivity is associated with pathological tau aggregates in dystrophic neurites around neuritic plaques and neurofibrillary tangles (inset a). In addition hypertrophic astroglial cells are labeled in AD brain (inset b). (B) Specificity of affinity-purified anti-AxoCT antibody. Panel a: COS7 cell lysate transfected with pEGFP-axoFL (lane 1), pEGFP-axoC2 (lane 2) and pEGFP (lane 3). Western blot analysis with anti-AxoCT antibody labels a 100 kDa protein in lane 1 corresponding to the GFP-axotrophin (aa 1-704) fusion protein and a 45 kDa protein in lane 2 corresponding to the GFP-axotrophin (aa 542-704) fusion protein. Endogenous axotrophin was undetectable. Panel b: PHF-tau prepared from temporal cortex of AD brain by the sarcosyl procedure was probed with antibodies Tau5/HT7 (lane 1) and anti-AxoCT (lane 2). Three immunoreactive bands corresponding to A68 PHF-tau were strongly labeled by the tau antibodies. The anti-AxoCT antibody does not cross-react with PHF-tau (lane 2). (C) Quantification of axotrophin in cytoplasmic and nuclear protein fractions obtained by differential protein extraction from temporal cortex (Brodmann area 22). Equal amount of protein was resolved by SDS-PAGE and labeled with a monoclonal axotrophin antibody. Signal intensity of the 80 kDa protein band was quantified by densitometry and revealed a significant loss of cytoplasmic and nuclear axotrophin protein in AD cases (Student's t-test, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). (D) Co-localization of axotrophin and neurofibrillary tangles in the hippocampus of AD brain. Axotrophin was labeled by the polyclonal anti-AxoCT antibody followed by Cy3-linked anti-rabbit secondary antibody (panel b) and for the detection of tau aggregates monoclonal tau antibody AT8 (1:500) was used followed by Cy2-linked anti-mouse secondary antibody (panel a). Fluorescence labeling was analyzed by confocal laser scanning microscopy. Axotrophin is colocalized with tau aggregates in hippocampal neurons (panel merge, scale bar: 20 μm).