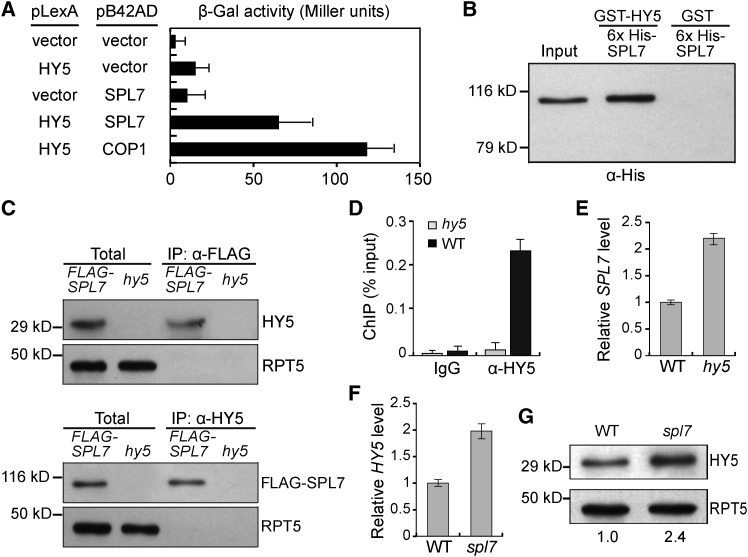
Figure 1.
Interaction of SPL7 and HY5.
(A) HY5 interacts with SPL7 in a yeast two-hybrid assay. The β-galactosidase activities resulted from the HY5-SPL7 interaction, and various controls are shown. The HY5-COP1 interaction (Ang et al., 1998) was used as a positive control. Error bars indicate sd (n = 4).
(B) HY5 can pull down SPL7 in vitro. Purified 6×His-tagged SPL7 was incubated with recombinant GST-HY5 or GST and immunoprecipitated with agarose beads conjugated with a GST antibody. The precipitates were subjected to immunoblotting using the anti-His antibody. Input, 5% of the purified SPL7 used in the pull-down assays.
(C) HY5 associates with SPL7 in vivo. Total protein extracts from 35S:FLAG-SPL7/spl7 seedlings were incubated with anti-FLAG or anti-HY5 antibody-conjugated agarose beads. The precipitates and total extracts were subjected to immunoblotting with antibodies against HY5 and FLAG, respectively. RPT5 was used as a control.
(D) Confirmation of HY5 binding to the SPL7 promoter by ChIP-qPCR. ChIP was performed in wild-type and hy5 seedlings with or without the anti-HY5 antibody. The resultant DNA was analyzed by quantitative PCR with the values normalized to their respective DNA inputs.
(E) and (F) RT-qPCR analyses of SPL7 (E) and HY5 (F) transcript levels. Reverse-transcribed cDNA from wild-type, hy5, or spl7 seedlings was examined by quantitative PCR with the values normalized to those of the wild type.
(G) Immunoblot analysis of HY5 protein levels in wild-type and spl7 seedlings. Values below the blots represent HY5 levels normalized against the loading control RPT5 using ImageJ and set to 1 for the wild type.