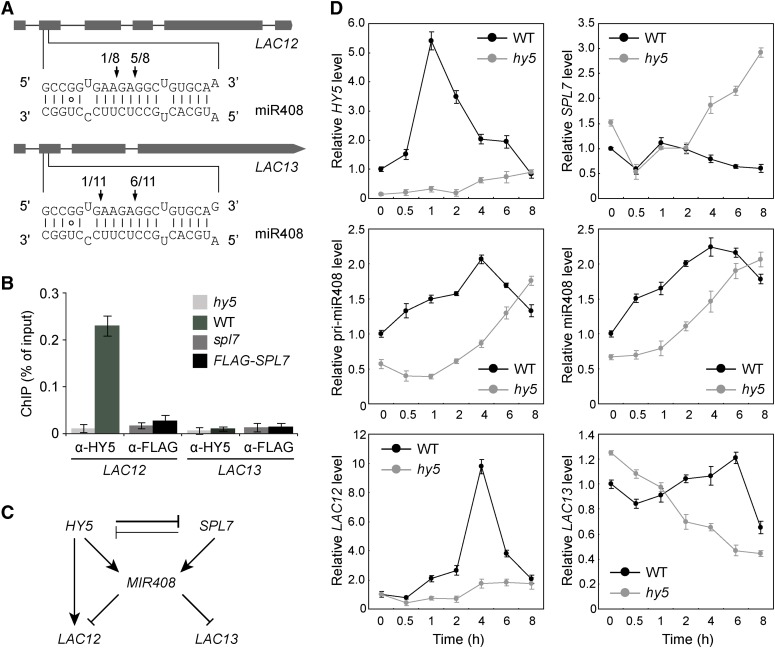
Figure 6.
The miR408 Target Genes LAC12 and LAC13 Are Differentially Regulated in the HY5-SPL7 Network.
(A) Confirmation of miR408 targeting on LAC12 and LAC13 by 5′ RNA ligase-mediated RACE. Gene structures of LAC12 and LAC13 are shown on the top, with shaded boxes representing exons. The complementary mRNA and miRNA sequences are shown on the bottom. Perfect base pairing is shown as vertical dashes, whereas G:U wobble pairing is indicated by circles. Vertical arrows mark the sequenced cleavage sites with the frequency of clones shown.
(B) Analysis of HY5 and SPL7 binding to the LAC12 and LAC13 promoters by ChIP-qPCR analysis. ChIP was performed in the indicated genotypes using either the anti-HY5 or anti-FLAG antibody. The resultant DNA was analyzed by quantitative PCR with the values normalized to their respective DNA inputs.
(C) Regulatory interactions among HY5, SPL7, MIR408, LAC12, and LAC13. Mutual inhibition between HY5 and SPL7 is based on the molecular data presented in Figure 1. The coordinated transcriptional regulation of MIR408 by HY5 and SPL7 is deduced from Figure 4. The regulation of LAC12 and LAC13 by miR408 at the posttranscriptional level and by HY5 at the transcriptional level is as indicated in (A) and (B), respectively.
(D) Quantitative analysis of HY5, SPL7, miR408, pri-miR408, LAC12, and LAC13 transcript levels in wild-type and hy5 seedlings. Seedlings were grown under the DC/LL condition, transferred to DC/HL at time 0, and assayed by RT-qPCR at the indicated time points thereafter.