Figure 3.
Calcium-Dependent Phospholipid Binding of CAR Proteins.
Ca2+ and CAR-dependent recruitment of PYR/PYLs to phospholipid vesicles was performed.
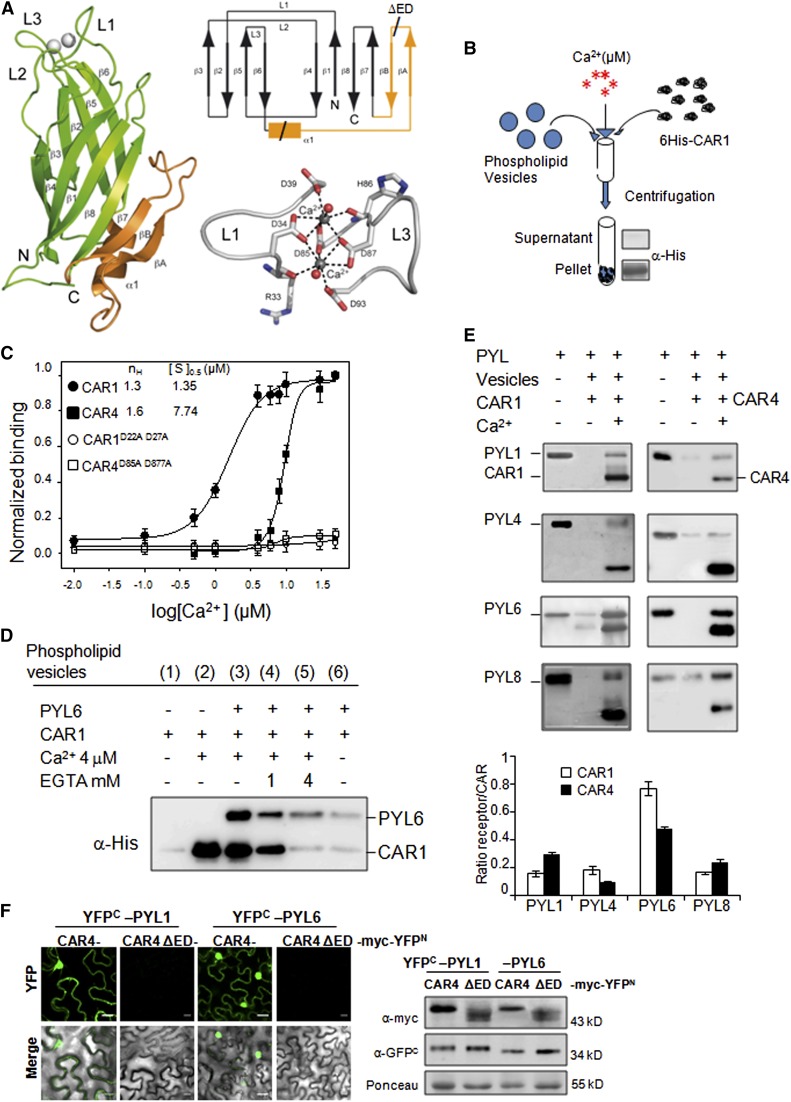
(A) Crystal structure, Ca2+ coordination, and topology of CAR4. A ribbon representation of the CAR4 crystal structure (left) showing overall fold together with a scheme of the topology (top right) and a detailed representation of the calcium binding sites (bottom right) are shown. The α1βAβB extra-domain is highlighted in orange.
(B) Scheme of the biochemical assay to detect Ca2+-dependent protein-phospholipid interaction through pelleting of phospholipid vesicles and immunoblot analysis. Phospholipid vesicles were composed of 25% phosphatidylserine and 75% phosphatidylcholine. The vesicles were precipitated by centrifugation, and bound proteins were revealed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblot analysis using α-His antibody.
(C) CAR1, CAR4, CAR1D22A D27A, and CAR4D85A D87A proteins were incubated with phospholipid vesicles in the presence of increasing concentrations of Ca2+ to determine the half-maximal binding for the ion. Introduction of two Asp-to-Ala mutations into amino acid residues 22 and 27 of CAR1 or residues 85 and 87 of CAR4 abolished phospholipid binding. The Hill coefficient (nH) and calcium concentration leading to half-maximal binding ([S]0.5) are indicated at the top of the graph.
(D) Ca2+- and CAR1-dependent recruitment of PYL6 to phospholipid vesicles. Ca2+- and CAR1-dependent vesicle pelleting of PYL6 can be reversed by EGTA treatment. Pelleted vesicles bound to PYL6 and CAR1 were EGTA treated, precipitated again by centrifugation, and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblot.
(E) Ca2+-dependent vesicle pelleting assay of CAR1 and CAR4 using different PYR/PYLs. The Ca2+ concentration was either 4 or 20 μM for CAR1 or CAR4, respectively. The quantification of the assays shows the relative ratio of receptor bound (minus background in the absence of calcium) per molecule of CAR1 or CAR4.
(F) A CAR4ΔED mutant is unable to interact with PYL1/PYL6 ABA receptors. A BiFC assay was performed in N. benthamiana epidermal cells coinfiltrated with Agrobacterium suspensions containing the indicated constructs and the silencing suppressor p19. Immunoblot analyses (at right) confirm the expression of myc-tagged CAR4/CAR4 ΔED and YFPC-tagged PYL1/PYL6 proteins in N. benthamiana epidermal cells. Bars = 20 μm.