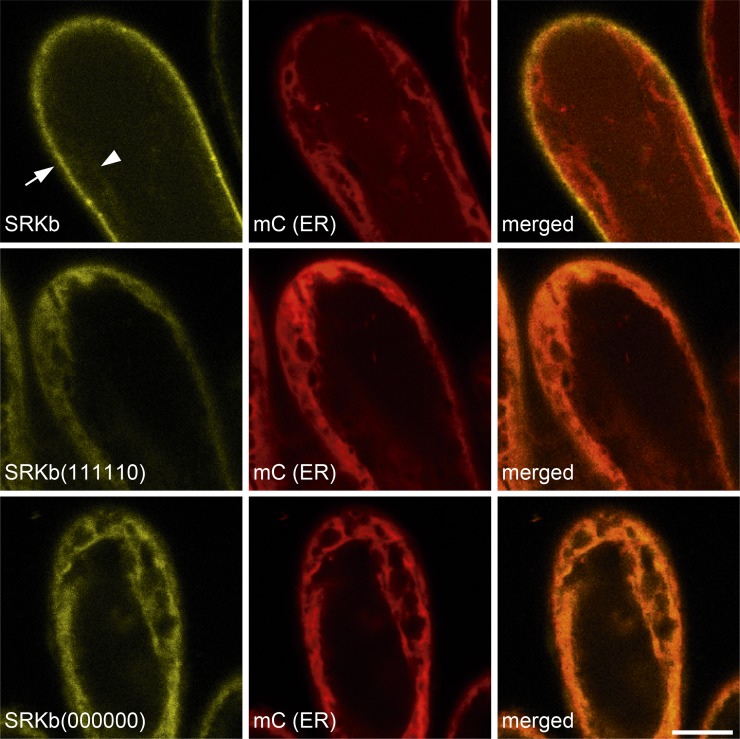
Figure 4.
Microscopic Analysis of the Effects of N-Glycosylation Site Mutations on the Subcellular Localization of SRKb.
The confocal microscopic images show the results of colocalization experiments of wild-type SRKb-cYFP, SRKb(000000)-cYFP, and SRKb(111110) proteins with an mCherry-labeled ER marker [mC (ER)] in stigma epidermal cells. The images show cYFP (yellow; left column), mC (red; middle column), and merged (right column) images that were captured for the same field of view. Note that wild-type SRKb-cYFP (top row) is primarily localized at the cell periphery (arrow), with only a weak signal observed in intracellular compartments (arrowhead), while the mutant SRKb(000000)-cYFP and SRKb(111110)-cYFP proteins are primarily localized in intracellular compartments (bottom two rows). Also note that the ER marker does not colocalize with the strong wild-type SRKb-cYFP but does colocalize perfectly with SRKb(000000)-cYFP and SRKb(111110)-cYFP proteins. The fact that the strong signals emanating from the ER marker, SRKb(000000)-cYFP, and SRKb(111110)-cYFP are distributed toward the outer edges of the protoplast reflects the presence of a large central vacuole that causes the cytoplasm and ER to be closely appressed to the PM in stigma epidermal cells, as in other plant cells. Bar = 10 μm.