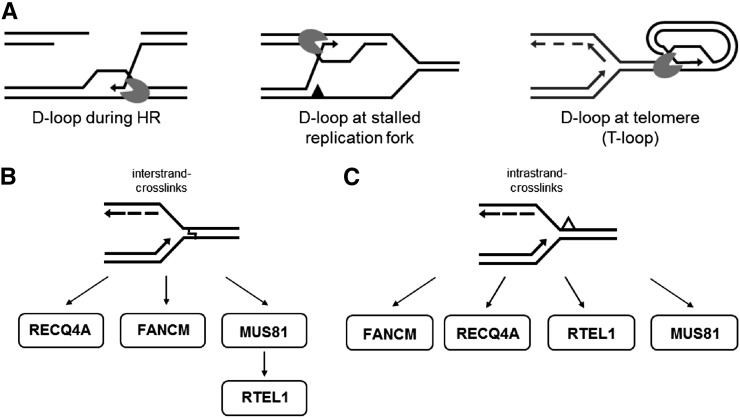
Figure 11.
Model of RTEL1 Functions in Arabidopsis.
(A) At D-loop-like structures that can be found during HR, at stalled replication forks, and at the telomeres, antirecombinases such as RTEL1 disrupt the D-loop by rejecting the invaded single strand. This opens the end of the chromosome for replication in the case of telomeres, or it enables annealing to the second end of a double strand break for repair via the synthesis-dependent strand-annealing pathway in the case of HR.
(B) During interstrand CL repair, RTEL1 acts downstream of MUS81, in a parallel pathway to FANCM and RECQ4A.
(C) During intrastrand CL repair, RTEL1 and MUS81 function in parallel pathways. Other pathways involve FANCM and RECQ4A.