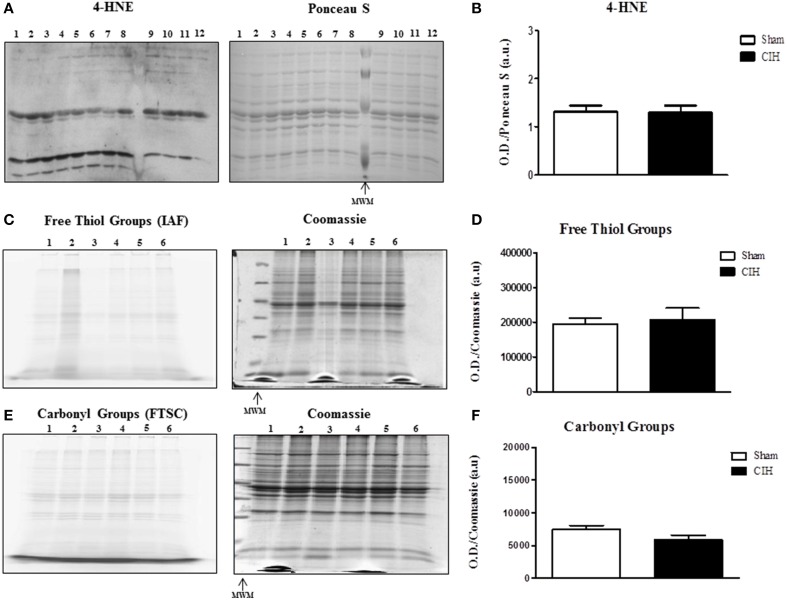
Figure 2.
Western blot of 4-HNE protein adducts and 1D electrophoresis to determine free thiol and carbonyl group content in the sternohyoid muscle from sham and chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH)-exposed rats. Sham and CIH samples were loaded in alternate lanes (numbered in the figure). (A) Sternohyoid 4-HNE content together with Ponceau S stained membrane. (B) Densitometric analysis of 4-HNE protein adduct band intensities normalized by densitometric intensities of corresponding Ponceau S stained proteins expressed in arbitrary units (a.u.) from sham and CIH-exposed rats. No significant difference was observed in 4-HNE protein adduct content (P = 0.9372; Student unpaired t-test) comparing sham and CIH-exposed sternohyoid muscles. Representative images of sternohyoid iodoacetamidofluorescein (IAF)-tagged protein free thiol groups (C) and fluorescein-thiosemicarbazide (FTSC)-tagged carbonyl groups (E) with corresponding coomassie stained membranes used to normalize protein loading and electrotransfer. Densitometric analysis of protein free thiol group (D) and carbonyl group (F) contents normalized by densitometric intensities of corresponding coomassie stained proteins expressed in arbitrary units (a.u.) from sham and CIH-exposed rats. Protein free thiol and carbonyl group content of the sternohyoid muscle was not significantly different in sham and CIH-exposed rats (P = 0.699 and P = 0.180 respectively; Student unpaired t-tests). Values are mean ± SEM; n = 6 per group.