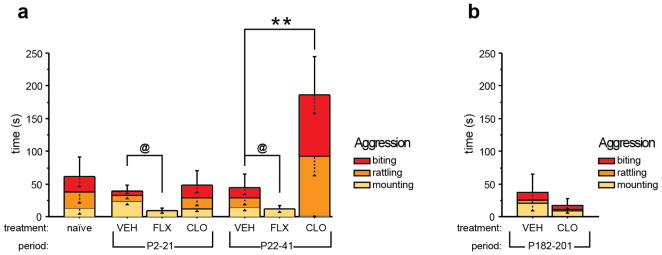
Fig. 2. Altered aggression after developmental 5-HTT or MAOA blockade.
Isolation induced aggressive behavior was assessed in mice by scoring the time spent mounting, tail rattling, or biting during a 10-minute encounter. (a) Aggressive behavior was increased in mice treated with CLO from P22-P41 when compared to control mice treated with VEH from P22-P41. Mice treated with FLX displayed reduced aggression when compared to VEH-treated control mice. Of note, FLX treated mice did not display any tail rattling or biting behavior. (n = 7–16 pairs per group). (b) Aggressive behavior was unaffected by transient CLO-treatment from P182-P201 (n = 7 pairs per group). (@ indicates main effect of treatment: p < 0.05; **p < 0.01).