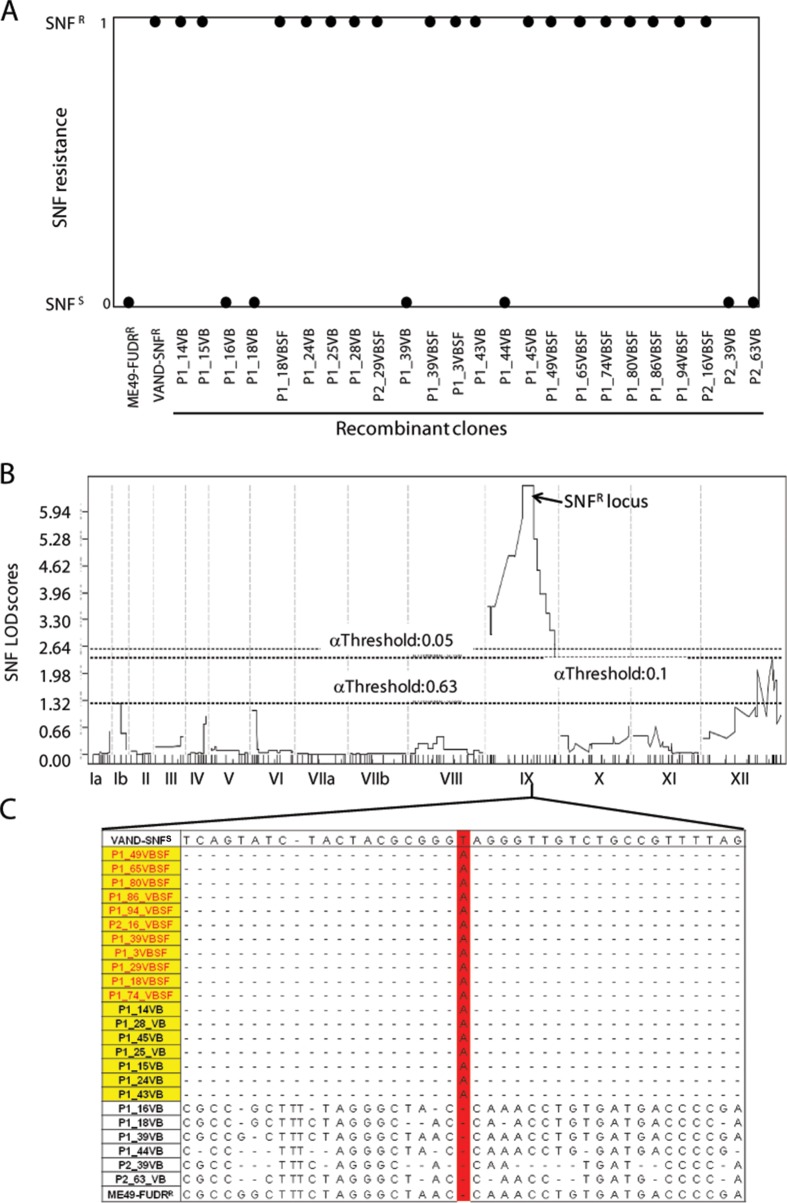
FIG 1.
Sinefungin resistance phenotype in the parents and progeny of the ME49-FUDRr × VAND-SNFr cross. (A) Cloned progeny were grown in the presence of 3 × 10−7 M SNF and assessed for the ability to grown in the presence of drug. All doubly drug-selected progeny (VBSF) and 7 of 13 non-drug-selected progeny were SNF resistant. Phenotypes are shown as a binary trait where SNFr is scored as 1 and SNFs is scored as 0. (B) QTL mapping of the SNF resistance phenotype produced a significant peak in the middle of chromosome IX with a LOD score of 6.57. Confidence thresholds based on 1,000 random permutations of the data are shown. (C) Genomic reads for the progeny were aligned to the VAND-SNFs reference genome, and SNPs were identified. The region on IX spanning the QTL peak was assessed for SNPs present in SNF-resistant progeny (yellow) and not present in the SNF-sensitive progeny. Doubly drug-resistant progeny are shown in red lettering. One SNP matching this pattern (highlighted in red) was found at position 3901106 on chromosome IX. A small region containing SNF locus SNPs surrounding the T → A mutation is shown.