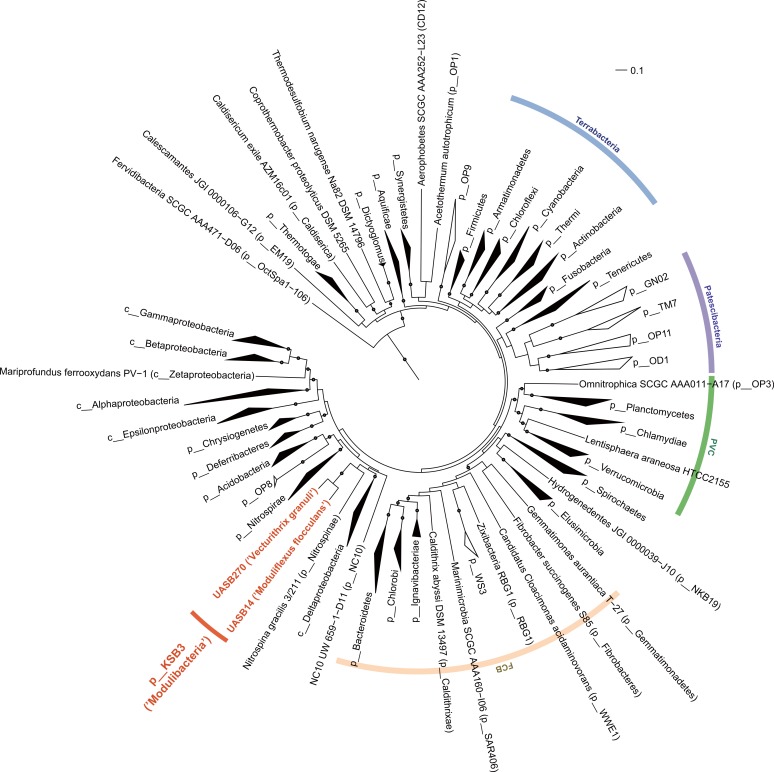
Figure 2. Maximum-likelihood phylogenetic inference of Modulibacteria (KSB3) population genomes among known bacterial phyla.
The tree was constructed using RAxML based on up to 38 marker genes (using taxon-outgroup configuration Config 3, Table S3) and sequences were collapsed at the phylum level except for classes in the Proteobacteria. Ranks are indicated by prefix; p__ (phylum), c__ (class). KSB3 genomes obtained in this study are highlighted in red. Superphyla (Terrabacteria, Patescibacteria, Fibrobacteres-Chlorobi-Bacteroidetes [FCB], and Planctomycetes-Verrucomicrobia-Chlamydiae [PVC]) are highlighted with color ranges. Taxa comprising cultivated representatives are shown in black; taxa with no cultivated representatives are indicated by outline. Reproducible associations (>80% bootstrap values from 100 resamplings) are indicated by dots on interior nodes. Alignments of homologous proteins from archaeal genomes were used to root the tree (not shown). The scale bar represents 10% estimated sequence divergence.