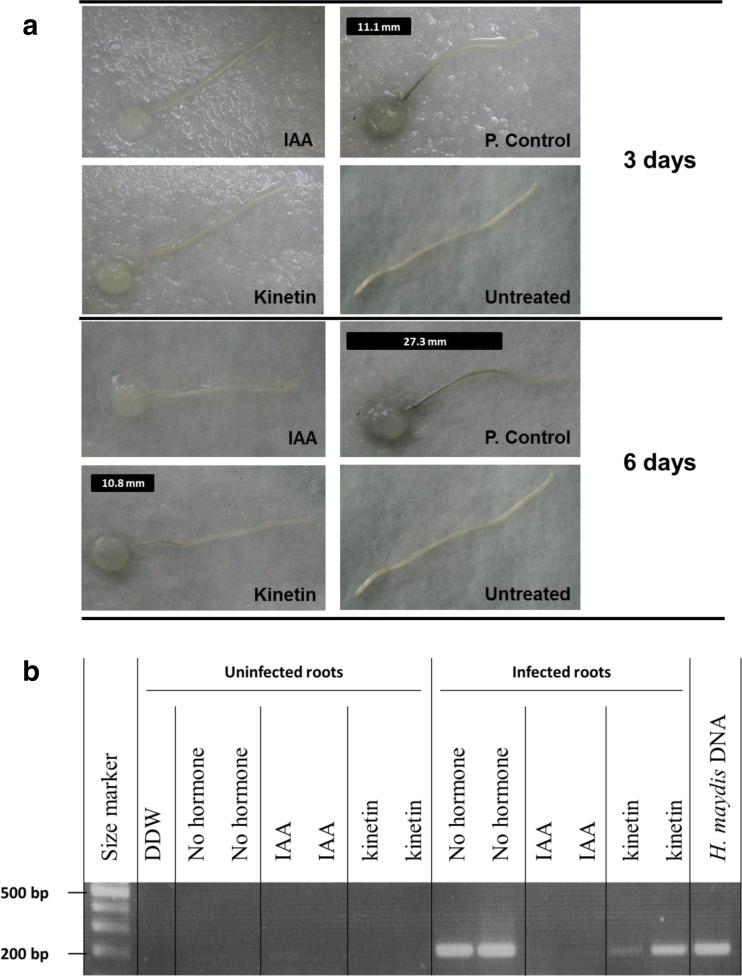
Fig. 2.
Detached root pathogenicity assay for the influence of auxin and kinetin on H. maydis. Side, young and white roots, about 2 cm long, were removed from potted 20-day-old maize seedlings (Zea mays L., Jubilee cv.) and inoculated by placing a 6-mm-diameter culture agar disk taken from the margins of a 4-6-day-old fungal colony (grown at 28 ± 1 °C in the dark) on the cut end of each root. The inoculated roots were placed separately in petri dishes containing auxin (IAA) or kinetin (100 mg/L) or distilled and deionized water, DDW (p. control), and incubated in moist petri dishes at 28 ± 1 °C in the dark. Negative controls are roots without pathogen inoculation inoculates on DDW without hormones (untreated). a. Progression of the pathogen infection thread inside the xylem tissue of each root (seen as a dark filament within the root) was evaluated qualitatively after three and six days of inoculation and marked in the photograph by a black line positioned above each root. b. In order to identify the fungus DNA in the above treated roots tissues, one segment was cut at 1 cm from the cut end of each root, six days after inoculation. DNA isolation and PCR were conducted for the presence of the pathogen using a PCR-based method, amplified at 200 bp H. maydis-specific oligonucleotide. Controls: DDW – distilled and deionized water, a negative control, used as a template in the PCR mixture to ensure the absence of DNA contamination; H. maydis DNA – positive control, obtained from an agar plate colony