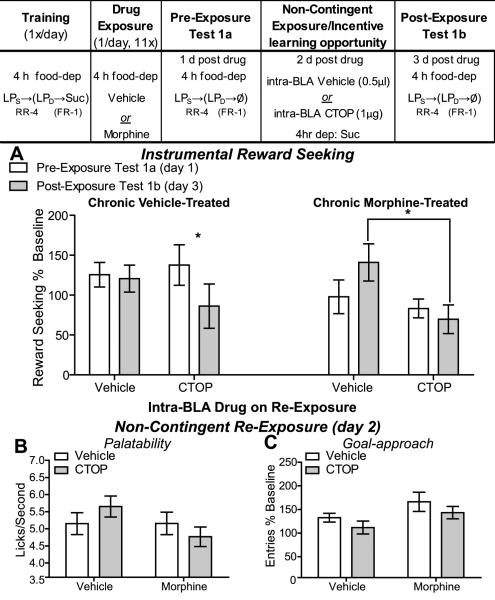
Figure 4. Experiment 4: Early Opiate withdrawal-induced inflated incentive value is dependent upon BLA mu opioid receptor activation.
Table: Experiment 4 Design- Rats were trained 4 h food deprived on a heterogeneous seeking-delivery chain of actions to earn sucrose. Following training rats were treated with either vehicle or morphine 1/d for 11 d. Testing commenced 24 h after the last drug injection and was conducted in early withdrawal. Rats were tested for the effects of opiate withdrawal on reward seeking (in 5 min non-rewarded extinction tests) both prior to and after non-contingent exposure to the sucrose training outcome in the opiate withdrawn state. During this incentive learning opportunity rats were given an infusion of either intra-BLA sterile water vehicle (vehicle-treated n=11, morphine-treated n=8) or CTOP (1µg/side; vehicle-treated n=8, morphine-treated n=9) to block mu opioid receptors. A. Effects of opiate withdrawal on reward seeking (normalized to pre-drug baseline reward-seeking response rate) prior to (Test 1a- open bars) and after (Test 1b- shaded bars) an opportunity to experience the sucrose training outcome in the opiate withdrawn state. B. Effects of early opiate withdrawal and intra-BLA CTOP on sucrose palatability, assessed as lick frequency, during the non-contingent re-exposure to the sucrose in opiate withdrawal. C. Effects of early opiate withdrawal and intra-BLA CTOP on goal approach (normalized to pre-drug baseline entry rate) during the non-contingent re-exposure to the sucrose in opiate withdrawal. RR-4, random-ratio 4; FR-1, fixed-ratio 1; LPS, seeking lever press, LPD, delivery lever press; Suc, 20% sucrose solution; Ø, no reward delivery; dep, deprived; *, p<0.05.