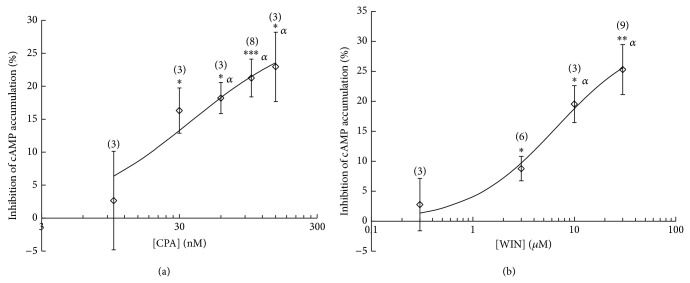
Figure 1.
Inhibition of forskolin-stimulated cAMP accumulation by CPA (a) and WIN55212-2 (b) in rat hippocampal slices. (a) Slices were incubated for 30 min in the presence of rolipram (50 μM) and adenosine deaminase (2 U/mL). After this period, incubation continued for a 15 min period in the absence (control) or in the presence of CPA (10–150 nM). Finally incubation proceeded in the presence of forskolin (10 μM) for a further 15 min period. (b) Slices were incubated for 45 min in the presence of rolipram (50 μM) and in the absence (control) or in the presence of WIN55212-2 (0.3–30 μM). After this period, incubation continued for a further 35 min period in the presence of forskolin (10 μM). Data are mean ± SEM of the % inhibition of control cAMP accumulation, corresponding to 3–9 independent experiments run at least in triplicate. The solid lines correspond to the nonlinear regression curves obtained by fitting a Michaelis-Menten type equation to the experimental points. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, and *** P < 0.001, when compared with zero, Student's t-test. αStatistically significant (P < 0.05) when comparing the cAMP accumulation obtained in the presence of CPA or WIN55212-2 with control cAMP accumulation (One-way ANOVA, followed by LSD test). The number of experiments corresponding to each concentration is indicated in brackets above the bars.