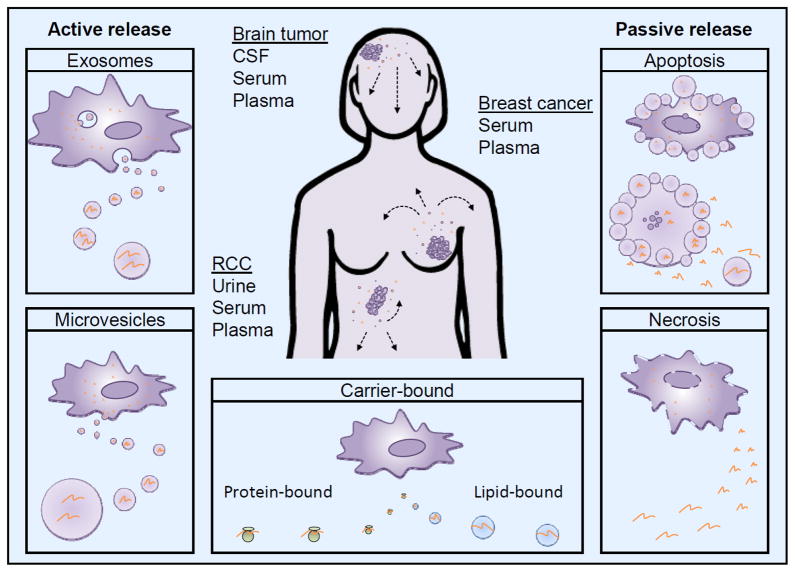
Figure 1. Cell-free miRNA secretion pathways.
Tumor-derived cell-free miRNAs can be released into the local microenvironment using multiple pathways from where they can potentially enter any body fluids. The most commonly used body fluids for miRNA detection of brain tumors, breast cancer and renal cell carcinoma (RCC) are illustrated. Exosome and microvesicle secretion are active processes whereby small membrane-enclosed vesicles containing a variety of molecules, including, proteins, DNA, and various RNA species, are released into the extracellular milieu. Cell death by apoptosis and necrosis passively leak cell-free miRNAs into the surrounding. Apoptotic bodies can also enclose miRNAs. Carrier-bound cell-free miRNAs can be bound by protein or lipid carriers; it is not understood how this release is mediated.