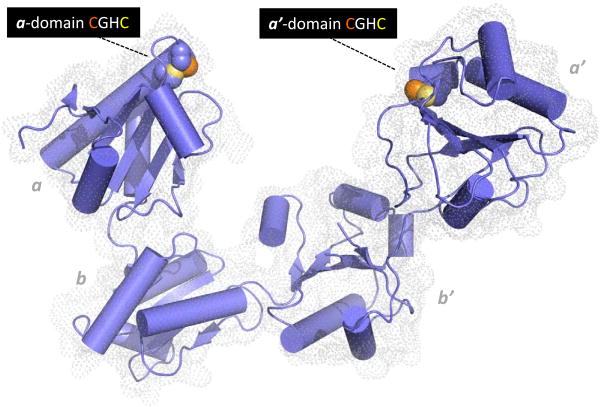
Figure 2.
Structure of human PDI. The coordinates for the oxidized protein are from Wang et al. [28]. Redox-active CxxC motifs are found in both a and a′ domains. The N-terminal cysteine sulfur atom of each motif (orange) is solvent accessible and engages in mixed disulfides with redox partners and proteins undergoing disulfide editing. The C-terminal cysteine by contrast is largely buried from solvent (yellow). The b and b′ domains are redox-inactive. Protein clients of PDI can occupy the central cavity with significant hydrophobic interactions with the b′ domain.