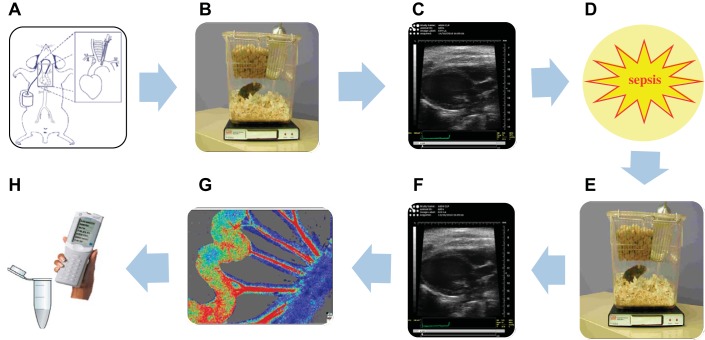
Fig. 6.
Schematic representation of multiparameter monitoring of sepsis progression in a single mouse. Following implantation of telemetry catheters (A), baseline hemodynamics are recorded remotely in unrestrained ambulatory mice (B). Basal cardiac function is measured under isoflurane anesthesia by echocardiography (C). Sepsis is then induced either by LPS or CLP (D), and hemodynamics (E) and cardiac function (F) are re-recorded in the same mice under pathological conditions. Mice are then terminally anesthetized at a time point of interest, and mesenteric blood flow is measured by laser speckle contrast imaging (G). Intravenous or topical drug administration may be used to determine vasoactivity. Mice are then terminated by venupuncture, and blood samples obtained from the inferior vena cava are analyzed by iSTAT point-of-care analyzer (H). Further biochemical and histological investigation may then be carried out.