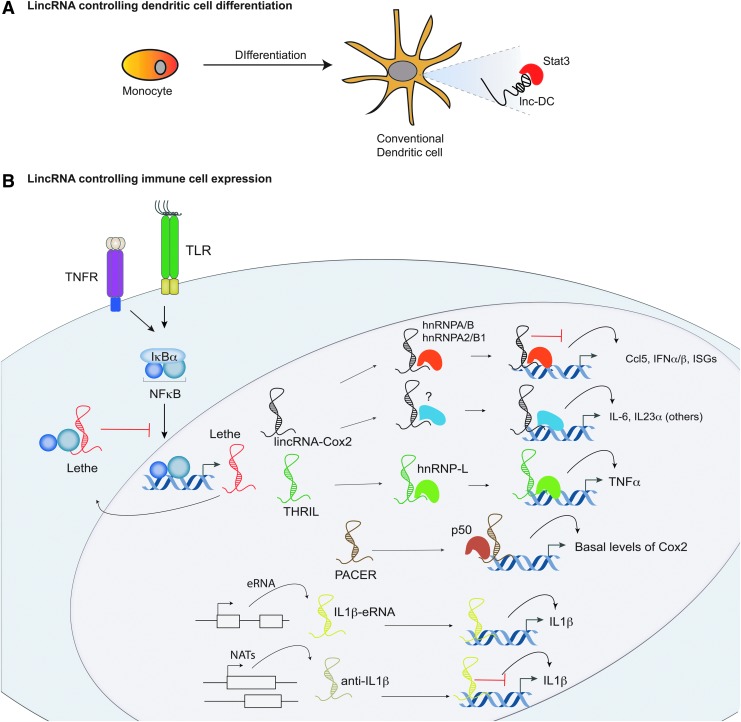
FIG. 3.
Long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) regulation within the Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling pathway. A, Lnc-dendritic cell (DC) is the first lncRNA identified to function in immune cell differentiation. Its role is in monocyte to conventional DC differentiation. B, Recent studies have identified lncRNAs that play critical roles in the TLR signaling pathway. LincRNA-Cox2 is required to maintain basal levels of interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs) through interactions with hnRNP-A/B and A2/B1. LincRNA-Cox2 also possesses activating functions and is critical for the induction of proinflammatory genes following microbial challenge. A long noncoding pseudogene RNA named Lethe can act as a negative regulator of TLR signaling. Lethe can bind to RelA, a subunit of NFκB heterodimeric complex preventing NFκB from binding to promoter regions of target genes. A lincRNA termed THRIL acts to regulate TNF-α expression in human monocytes through its interactions with hnRNP-L. LincRNA PACER controls basal levels of Cox2 (PTGS2) through binding to the p50 subunit of NFκB. An enhancer RNA termed IL1β-eRNA functions to positively regulate IL1β production in human monocytes. Finally overexpression of a natural antisense transcript anti-IL1β inhibits IL1β production through alteration of the chromatin structure surrounding the IL1β promoter.