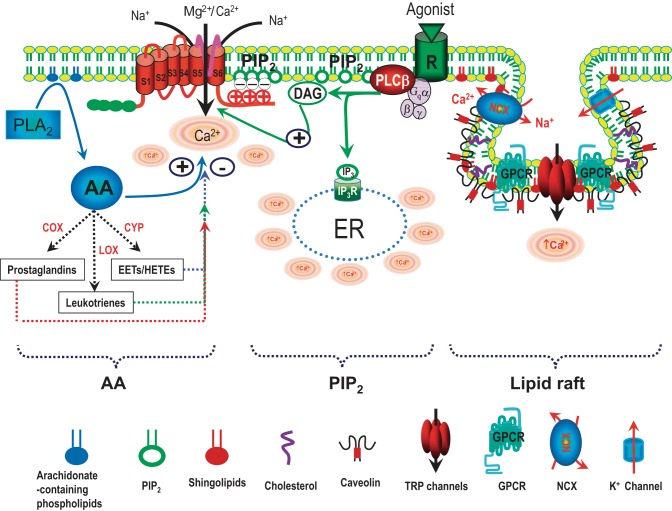
Fig. 3.
Schematic diagram of regulation of TRP channels by phospholipids and lipid rafts. TRP channels can be modulated by various phospholipids, including arachidonic acid (AA) generated by PLA2, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2), and lipids in the lipid rafts. AA can be metabolized through 3 enzymatic pathways: 1) the cyclooxygenase (COX) pathway produces prostaglandins; 2) the lipoxygenase (LOX) pathway yields monohydroxy compounds and leukotrienes; and 3) the cytochrome P-450 (CYP) epoxygenase pathway generates hydroxyleicosatetraenoic acids (HETES) and epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs). PIP2 is a co-activator of many TRP channels. Diaglycerol (DAG) generated by hydrolyzing PIP2 via Gq-linked receptor stimulation activates TRPC3 and TRPC6. Lipid rafts are specific microdomains orchestrating various signaling pathways, including GPCR, ion channels, and caveolin-1 (endothelial cells), or caveolin-3 (myocytes). Caveolae are a special type of lipid raft. Lipid rafts are enriched with cholesterol and sphingolipids. Disruption of lipid rafts by depletion of cholesterol or knockdown of caveolin alters TRP channel function within the rafts. Modified from Yue et al. (359).