Fig 4.
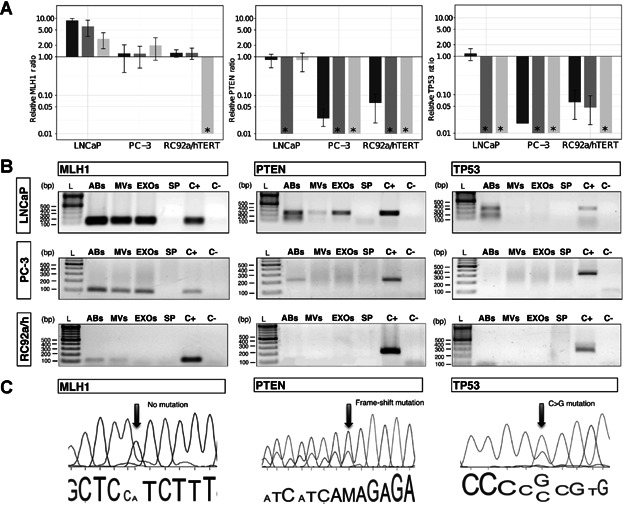
Presence of mutated DNA fragments in EV subpopulations. A: Relative ratio of MLH1, PTEN, and TP53 genomic DNA (gDNA) fragments assessed by qPCR from subpopulations of EVs derived from LNCaP, PC-3, and RC92a/hTERT cells, using GAPDH as a reference gene. The GAPDH gene was used as reference due to its constant presence in all the vesicle types (Supplementary Fig. S2). Asterisk (*) represents that the gene of interest was not detectable by qPCR or not present in the samples analyzed. Columns are the average of three experiments, each one measured in triplicates. Error bars represent SE. Apoptotic bodies: dark gray; microvesicles: gray; exosomes: light gray. B: Agarose gel electrophoresis of MLH1, PTEN, and TP53 gDNA fragments extracted of EVs derived from LNCaP, PC-3, and RC92a/hTERT cells (n = 3). Ladder (L), apoptotic bodies (ABs), microvesicles (MVs), exosomes (EXOs), supernatant from the last ultracentrifugation (SP), positive cell control (C+) and negative control (C−). C: Electropherograms displaying PTEN and TP53 mutations in ABs and EXOs. Part of genomic DNA sequences of MLH1, PTEN, and TP53 genes from LNCaP-derived vesicles, with no MLH1 mutation (left), PTEN mutation in codon 6 (Frame-shift mutations, delAA) (center) and TP53 mutation in codon 215 (CCC to CGC) (right). The arrows show the position of the mutations.
