Abstract
Packed erythrocytes are ideally suited as a model system for the study of water diffusion in biological tissue, because cell size, membrane permeability, and extracellular volume fraction can be varied independently. We used a pulsed-field-gradient spin echo NMR technique to measure the time-dependent diffusion coefficient D(t) in packed erythrocytes. The long-time diffusion constant, D(eff), depends sensitively on the extracellular volume fraction. This may explain the drop in D(eff) during the early stages of brain ischemia, where just minutes after an ischemic insult the extra-cellular volume in the affected region of the brain is significantly reduced. Using an effective medium formula, we estimate the erythrocyte membrane permeability, in good agreement with measurements on isolated cells. From the short-time behavior of D(t), we determine the surface-to-volume ratio of the cells, approximately (0.72 micron)-1.
Full text
PDF

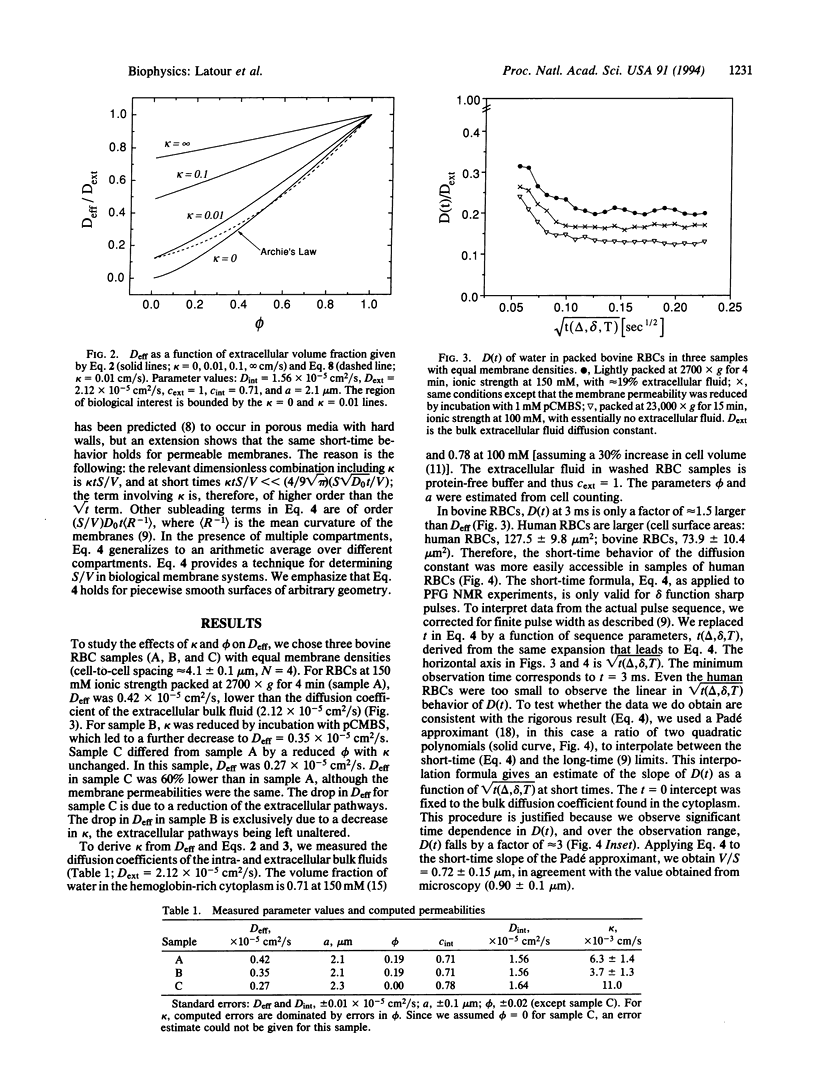
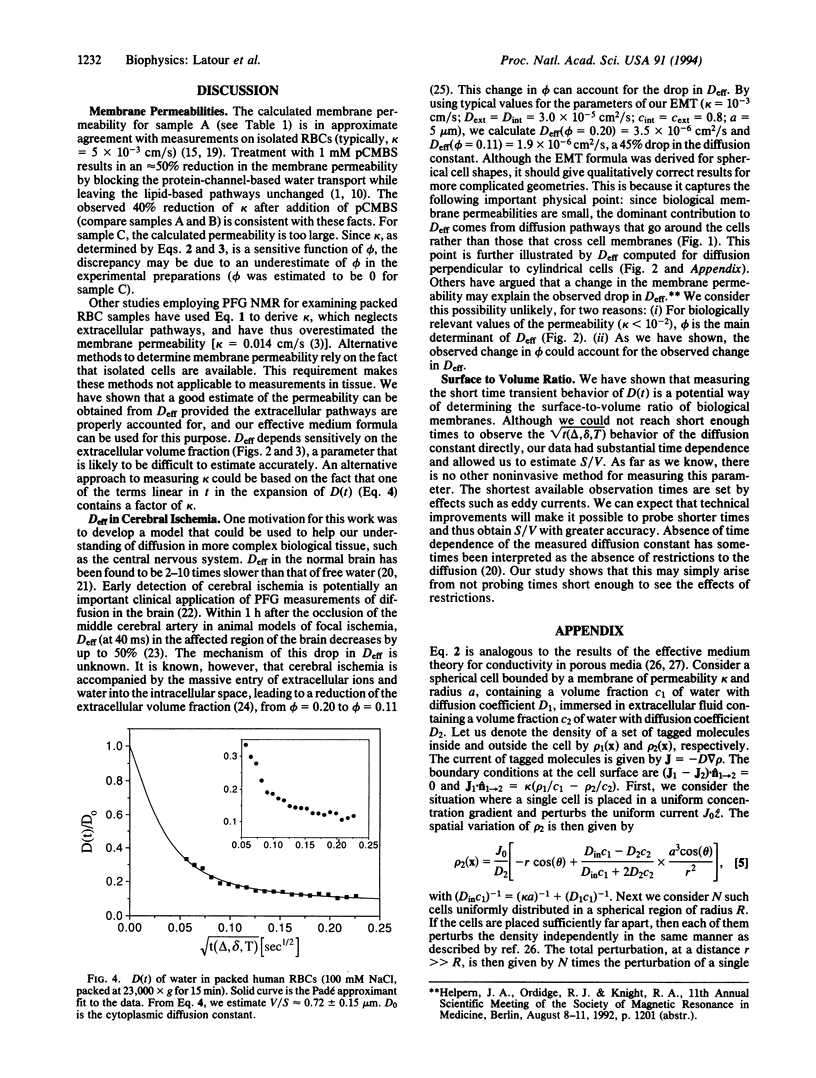

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cooper R. L., Chang D. B., Young A. C., Martin C. J., Ancker-Johnson D. Restricted diffusion in biophysical systems. Experiment. Biophys J. 1974 Mar;14(3):161–177. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(74)85904-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crick F. Diffusion in embryogenesis. Nature. 1970 Jan 31;225(5231):420–422. doi: 10.1038/225420a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endre Z. H., Kuchel P. W., Chapman B. E. Cell volume dependence of 1H spin-echo NMR signals in human erythrocyte suspensions. The influence of in situ field gradients. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Mar 23;803(3):137–144. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(84)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer R. E., Macey R. I. Perturbation of red cell volume: rectification of osmotic flow. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jan 6;196(1):53–65. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90165-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. H., Anderson M. L. Physiopathology of cerebral ischemia. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 1989;4(4):303–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajnal J. V., Doran M., Hall A. S., Collins A. G., Oatridge A., Pennock J. M., Young I. R., Bydder G. M. MR imaging of anisotropically restricted diffusion of water in the nervous system: technical, anatomic, and pathologic considerations. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1991 Jan-Feb;15(1):1–18. doi: 10.1097/00004728-199101000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klösgen B., Schönert H., Deuticke B. Measurement of rapid membrane permeation in cell suspensions by application of a generalized capillary method. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Mar 22;939(1):29–39. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight R. A., Ordidge R. J., Helpern J. A., Chopp M., Rodolosi L. C., Peck D. Temporal evolution of ischemic damage in rat brain measured by proton nuclear magnetic resonance imaging. Stroke. 1991 Jun;22(6):802–808. doi: 10.1161/01.str.22.6.802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bihan D., Turner R., Douek P., Patronas N. Diffusion MR imaging: clinical applications. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1992 Sep;159(3):591–599. doi: 10.2214/ajr.159.3.1503032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macey R. I., Farmer R. E. Inhibition of water and solute permeability in human red cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jul 7;211(1):104–106. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90130-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitra PP, Sen PN, Schwartz LM, Le Doussal P Diffusion propagator as a probe of the structure of porous media. Phys Rev Lett. 1992 Jun 15;68(24):3555–3558. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.68.3555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley M. E., Cohen Y., Mintorovitch J., Chileuitt L., Shimizu H., Kucharczyk J., Wendland M. F., Weinstein P. R. Early detection of regional cerebral ischemia in cats: comparison of diffusion- and T2-weighted MRI and spectroscopy. Magn Reson Med. 1990 May;14(2):330–346. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910140218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redwood W. R., Rall E., Perl W. Red cell membrane permeability deduced from bulk diffusion coefficients. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Dec;64(6):706–729. doi: 10.1085/jgp.64.6.706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuier F. J., Hossmann K. A. Experimental brain infarcts in cats. II. Ischemic brain edema. Stroke. 1980 Nov-Dec;11(6):593–601. doi: 10.1161/01.str.11.6.593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon A. K. Water channels across the red blood cell and other biological membranes. Methods Enzymol. 1989;173:192–222. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(89)73013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svoboda K., Schmidt C. F., Branton D., Block S. M. Conformation and elasticity of the isolated red blood cell membrane skeleton. Biophys J. 1992 Sep;63(3):784–793. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81644-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner J. E. Intracellular diffusion of water. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Jul 15;224(2):416–428. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90228-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]