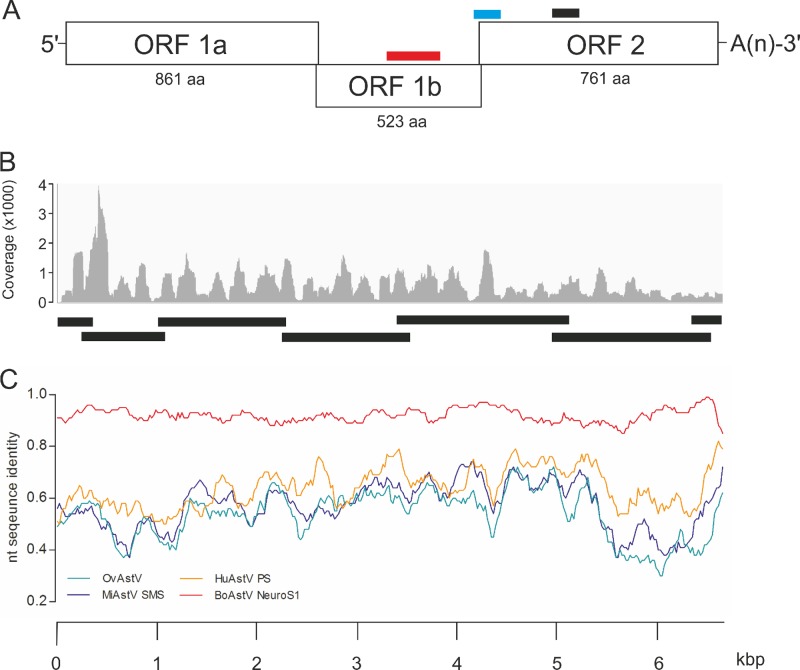
FIG 1.
Identification of the novel bovine astrovirus BoAstV-CH13 in the brain tissue of a cow with nonsuppurative encephalitis. (A) The viral genome is composed of 3 open reading frames (ORFs), short 5′ and 3′ untranslated regions (UTRs), and a poly(A) tail [-A(n)]. ORF1a and ORF1b encode nonstructural proteins, and ORF2 encodes structural proteins. The numbers of amino acids (aa) in each translation product are shown. Bars, target sequences for ISH (blue, probe A; black, probe B) and RT-PCR (red). (B) Assembly of NGS reads revealed a contig of 6,540 nt that included the entire coding region of the viral genome. The graph presents the average coverage of this contig for each nucleotide. Bars, fragments that were confirmed by Sanger sequencing. (C) Whole-genome sequences of BoAstV-CH13 (reference), ovine astrovirus (OvAstV), and astroviruses isolated from brain tissues of mink (MiAstV-SMS), a human patient (HuAstV-PS), and a steer in the United States (BoAstV-NeuroS1) were compared by sliding window pairwise identity plots. Scale, nucleotide positions within the astrovirus genome.