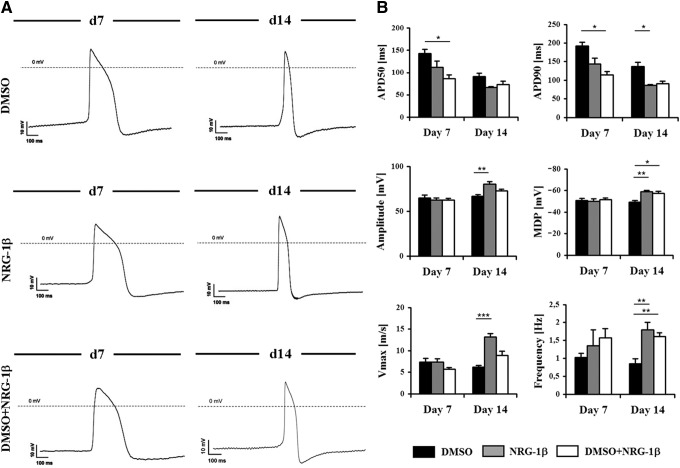
FIG. 3.
Electrophysiological properties of iPS-CMs. (A) Phenotype of iPS-CMs. Cells were differentiated by treatment with DMSO and/or NRG-1β. The electrophysiological properties were analyzed at day 7 and 14 of differentiation. Spontaneous action potential (AP) recordings indicated that ventricular-like differentiation had occurred in all of the experimental groups. (B) Electrophysiological maturation of iPS-CMs. APD50, APD90, amplitude, maximal diastolic potential (MDP), Vmax, and frequency parameters were measured at day 7 and 14. Measurements (n=10–14) were performed in several beating clusters from each experimental group. Even though the AP parameters of iPS-CMs were consistent with cultivated fetal CMs, more mature electrophysiological properties were associated with NRG-1β-treated CMs. Results are shown as mean±SD. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, and ***P<0.001 in comparison with DMSO.