Figure 2.
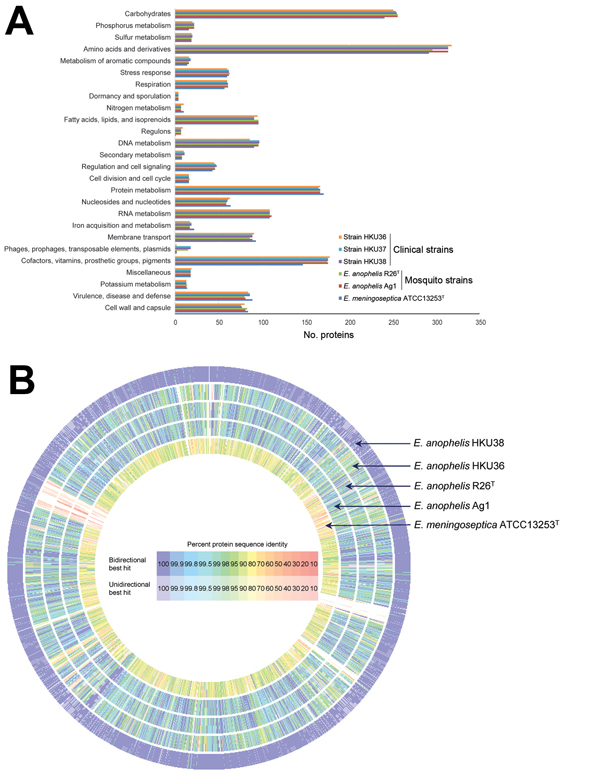
Comparison of draft genome sequence data of the 3 Elizabethkingia anophelis strains from patients in Hong Kong (HKU36–38), E anophelis type strain R26T, and E. meningoseptica type strain ATCC 13253T. A) Distributions of predicted coding sequence function in genomes of E. anophelis strains HKU36–38, E. anophelis type strain R26T, and E. meningoseptica type strain ATCC 13253T according to SEED Subsystems are shown. The columns indicate the number of proteins in different subsystems. B) Circular representation of sequence comparison between the draft genome of strain HKU37 and other draft genomes as labeled. Comparison generated in Rapid Annotations using Subsystem Technology (27). Intensity of color indicates degree of protein identity.
