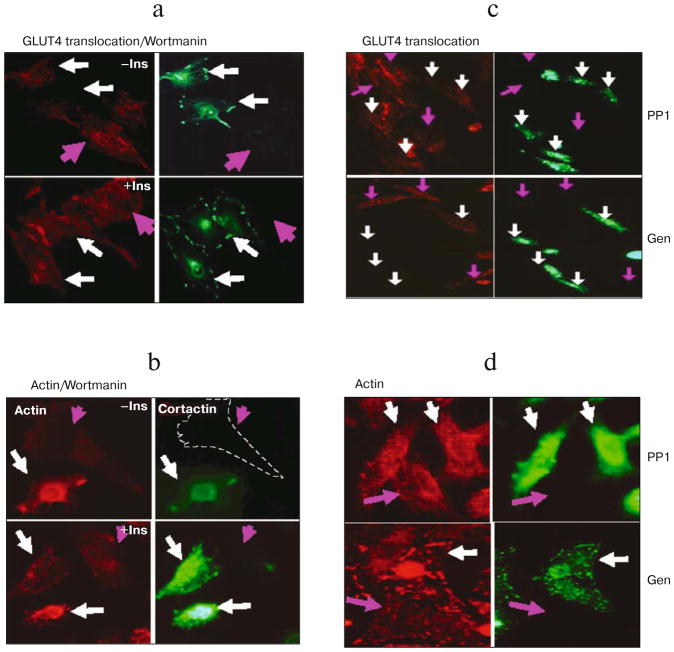
Fig. 6.
Effect of PI3 kinase and Src inhibitions on actin filaments and GLUT4 translocation. L6-GLUT4myc cells were transiently transfected with WT cortactin GFP cDNA (white arrows). a) Wortmannin, a PI3-K inhibitor, completely inhibits insulin-triggered GLUT4 translocation in L6-GLUT4myc cells with and without (pink arrows) overexpression of WT cortactin. Upper panels show unstimulated cells, lower panels show cells treated with 300 nM insulin for 10 min (a, b). b) Insulin-induced stress fiber formation in L6-GLUT4myc cells. Treatment with 0.3 μM wortmannin completely blocked actin stress fiber formation in both cells overexpressing wild type cortactin (white arrows) or untransfected cells (pink arrows). c) PP1 (upper panels) and genistein (lower panels), Src family protein kinase inhibitors, completely inhibit insulin-induced GLUT4 translocation in cells with (white arrows) and without (pink arrows) the overexpression of wild type cortactin. Cells were pretreated with 10 μM PP1 or 100 μM genistein and then treated with 300 nM insulin for 10 min. d) The insulin-induced formation of actin stress fibers in L6-GLUT4myc cells with or without overexpression of WT cortactin was also completely blocked by treatment with PP1 and genistein. Green fluorescence indicates GFP, red fluorescence indicates GLUT4myc or phalloidin staining.