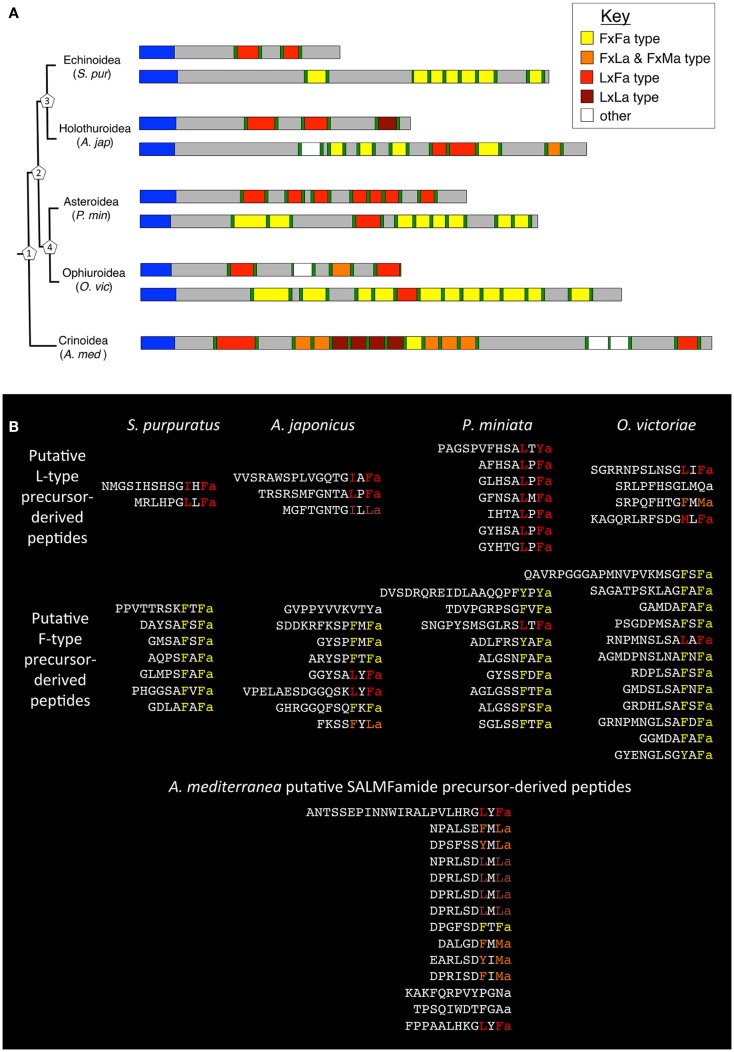
Figure 4.
The occurrence and properties of SALMFamide precursors (A) and putative SALMFamide peptides (B) in species representing each of the five extant echinoderm classes. (A) SALMFamide precursors are shown in a phylogenetic diagram according to the phylogeny of Telford et al. (18) and O’Hara et al. (21), with crinoids basal to the Echinozoa (Holothuroidea and Echinoidea) and the Asterozoa (Asteriodea + Ophiuroidea). The estimated divergence times for the nodes (labeled with numbers in pentagons) according to O’Hara et al. (21) are: 1. 501-542 Ma, 2. 482-421 Ma, 3. 464-485 Ma, and 4. at least 479 Ma. S. pur is the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus (Echinoidea), A. jap is the sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus (Holothuroidea), P. min is the starfish Patiria miniata (Asteroidea), O. vic is the brittle star Ophionotus victoriae (Ophiuroidea), and A. med is the feather star Antedon mediterranea (Crinoidea). Signal peptides are shown in blue and dibasic or monobasic cleavage sites are shown in green. L-type SALMFamides with a C-terminal LxFamide motif or with an L-type-like motif (e.g., IxFamide) are shown in red. F-type SALMFamides with a FxFamide motif or with an F-type-like motif (e.g., YxFamide) are shown in yellow. SALMFamides with a FxLamide-type motif are shown in orange and SALMFamides with a LxLamide motif are shown in dark red. Peptides that do not conform with any of the four color-coded categories are shown in white (e.g., GVPPYVVKVTYamide in A. japonicus and SRLPFHSGLMQamide in O. victoriae). The diagram shows how in a presumed ancestral-type precursor in crinoids the majority of the putative peptides have a FxLamide-type motif or a LxLamide-type motif and there is only one L-type SALMFamide and one F-type SALMFamide. However, as a consequence of specialization following a presumed duplication of the ancestral-type gene in a common ancestor of the Echinozoa and Asterozoa, two types of SALMFamide precursor have evolved: one that is predominantly comprised of L-type SALMFamides (red) and another that is exclusively or predominantly comprised of F-type SALMFamides (yellow). (B) C-terminal alignments of SALMFamide neuropeptides derived from the precursor proteins shown in (A). The C-terminal regions of each peptide are color-coded according to the key shown in (A).