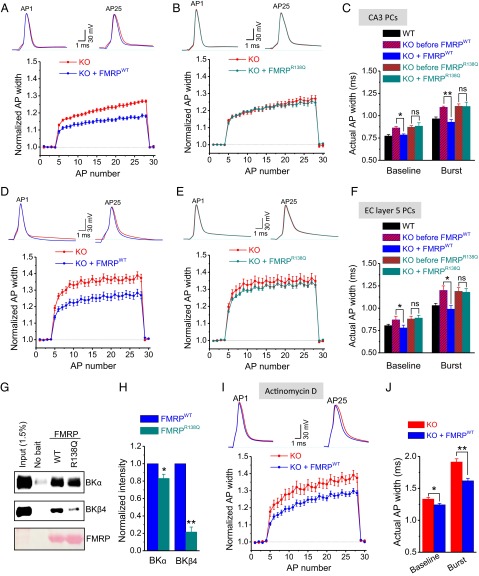
Fig. 4.
R138Q mutation impairs presynaptic function in mouse central neurons. Effect of intracellular perfusion of WT-FMRP298 (A) or R138Q-FMRP298 (B) on AP duration in Fmr1 KO CA3 pyramidal neurons before (0.2 Hz) and during 25 stimuli at 62.5 Hz. In each condition, AP duration during trains was normalized to four immediately preceding baseline measurements. (C) Actual AP width in different conditions is quantified. AP duration measurements in WT mice (n = 8) are provided as a reference. (D–F) Same as A–C for Fmr1 KO layer 5 entorhinal cortex (EC) pyramidal neurons, except 25-AP trains at 60 Hz were used. WT AP measurements (n = 9) in F are reanalyzed, in part, from our earlier study (18). (G) In vitro binding assay with His-tagged WT-FMRP298 or R138Q-FMRP298. Brain lysates from WT mice were incubated with His-tagged protein fragments or no bait as a control, and the levels of BK channel α- and β4-subunits bound to FMRP fragments were analyzed by Western blot with the indicated antibodies. (Top and Middle) Representative Western blots from n = 4 experiments (n = 5 for β4-subunit measurements) are shown. (Bottom) Ponceau staining is shown as control for an equal amount of His-tagged WT-FMRP298 or R138Q-FMRP298 used in this assay. (H) Quantification of G. (I–J) Effect of intracellular perfusion of WT-FMRP298 on AP duration at baseline and during 25-AP trains at 60 Hz in Fmr1 KO CA3 pyramidal neurons in the presence of transcription inhibitor actinomycin D (40 μM) with at least 1 h of preincubation. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.