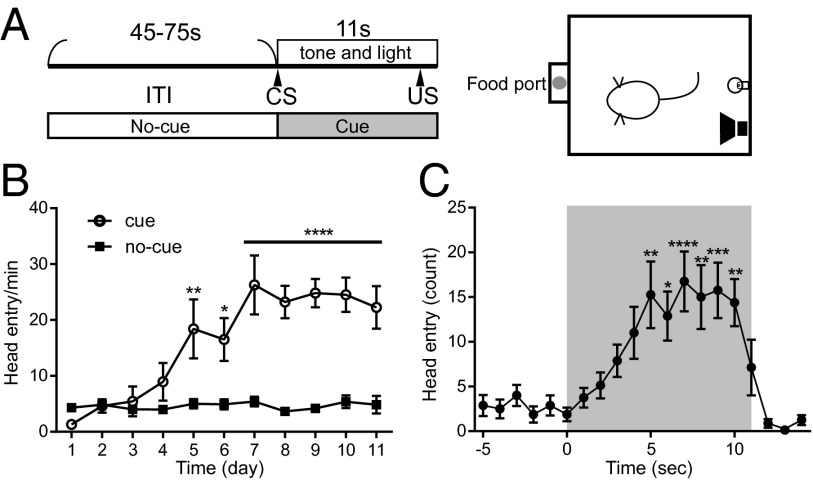
Fig. 1.
Behavioral paradigm used for assessing reward-approach behavior. (A, Left) Design of one trial. Each session contained 25 trials. (A, Right) Operant chamber. Food delivery was associated with tone and light presentation. (B) Learning of cue-food association and development of food magazine approach behavior. Mean (± SEM) head entry activity across sessions for eight subjects is shown. Head entry activity during the cue presentation period (○) and head entry during the ITI (■) are shown. The x axis represents training days, and the y axis represents averaged head entry activity. (C) Mean (± SEM) head entry activity during the prepresentation, cue presentation, and postpresentation periods (n = 8). Each dot represents the cumulated number of head entries observed in one session. The x axis represents seconds from the onset of the cue, and the y axis represents averaged head entry activity. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.