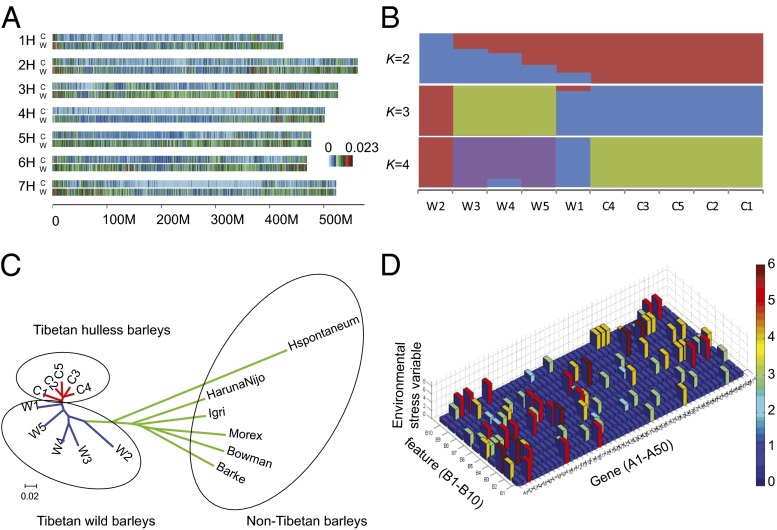
Fig. 3.
Population genetics of barleys. (A) SNP rate distribution for Tibetan wild barleys (W) and Tibetan hulless barley (C) across the seven chromosomes. There are 10 individuals including five Tibetan wild barleys and Tibetan hulless barleys. (B) STRUCTURE analysis of the 10 barley individuals. W1–W5 refer to five wild samples, and C1–C5 refer to five cultivated samples. (C) The neighbor-joining tree of barleys. The green lineages refer to six non-Tibetan barleys. The blue lineages refer to five Tibetan wild barleys. The red lineages refer to five Tibetan hulless barleys. (D) The adaptive correlation of randomly selected genes from SI Appendix, Table S34 (A1–A50) with 10 stressful environmental variables (B1–B10). The ecologically stressful variables include salinity, oxygen (low and high), solar radiation (especially high), CO2, drought, temperature (high and low), day length (short or long), and dormancy. The A1–A50 genes demonstrating adaptive correlation with environmental stress are directly or indirectly affecting other genes or gene networks related to metabolite cycles and other biological vital functions. Direct effects result in high correlations; indirect effects result in low correlations.