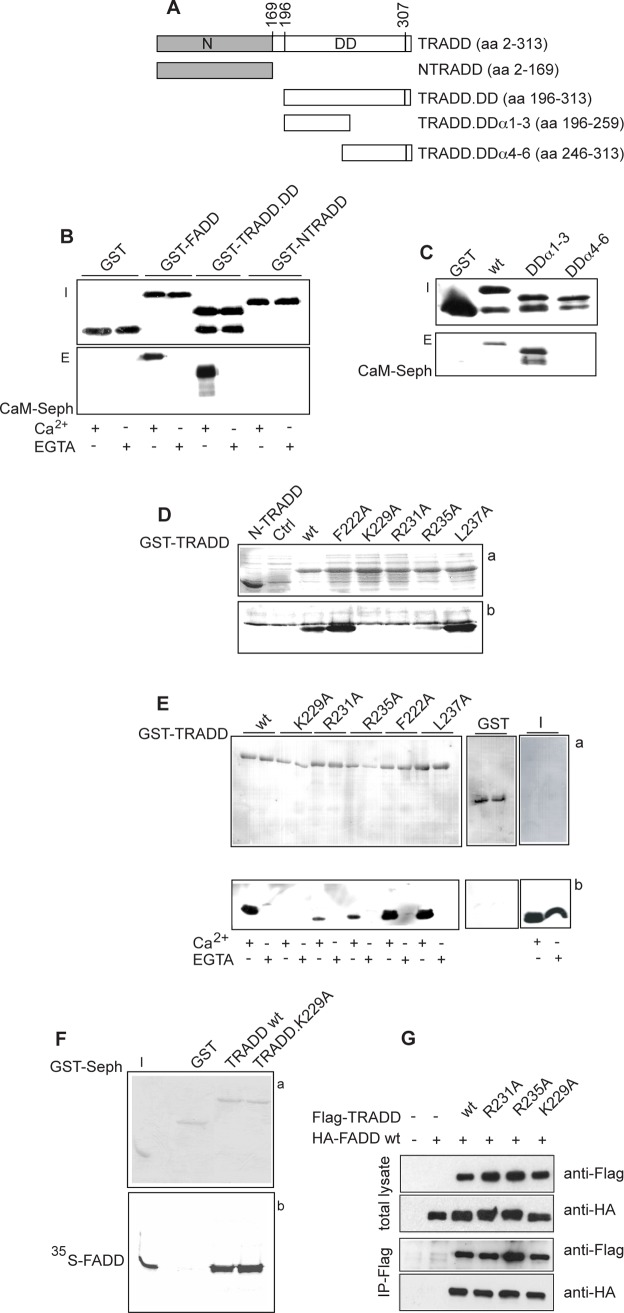
Figure 2. Characterization of a CaM binding site in TRADD.DD.
A: schematic representation of the GST-TRADD mutants. The N-terminal domain (N) and the Death Domain (DD) of human TRADD are indicated. B and C: western blot with GST specific antibody of GST-TRADD mutants (top panels, I stands for inputs) and CaM pull-down assays (bottom panels, E stands for eluates). The GST fusion proteins indicated were pull-down with CaM-sepharose beads in binding buffer with 2 mM Ca2+ (B, C) or EGTA (B). D: CaM blot overlay assay. E coli BL21 lysates expressing N-TRADD (lane 1) or untransformed (Ctrl) (lane 2) were used as negative controls. Top panel a) shows the ponceau stained filter and bottom panel b) the western blot probed with biotin-conjugated His-CaM. E: GST-TRADD pull-down assays. The GST-TRADD proteins indicated, bound to glutathione-sepharose beads, were incubated with His-CaM in binding buffer with 2 mM Ca2+ or EGTA. Top panel a) shows the ponceau stained filter and bottom panel b) the western blot probed with CaM specific antibody. I indicates the input of His-CaM. F: GST-TRADD pull-down assays. Bound proteins were analyzed by 12% SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. Panel a) shows the coomassie stained gel where I indicates the input of 35S-FADD. Panel b) shows the corresponding autoradiogram. G: Immunoprecipitation (IP) assay. Total lysates of Hek 293T cells expressing HA-FADD and Flag-TRADD proteins were probed with Flag or HA monoclonal antibodies. Cell lysates were IP with Flag-resin, as described in material and methods. The data shown are representative of at least three independent experiments.