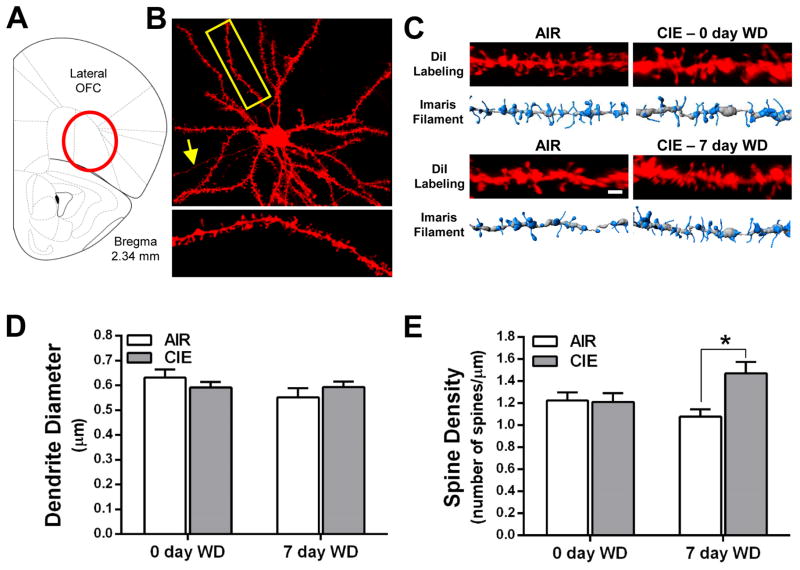
Figure 2.
Withdrawal from CIE exposure increases total spine density of layer II/III neurons in the lateral OFC. (A) Schematic depicting the OFC with the lateral OFC highlighted as the target brain region. (B) An example of a lateral OFC layer II/III pyramidal neuron filled with DiI. The yellow box and associated enlarged image provide an example of a second order dendritic segment and its dendritic spines. (C) Representative images and 3D models generated in Imaris XT at the 0 day (top panel) and 7 day (bottom panel) withdrawal time points. (D) CIE exposure and withdrawal did not alter the diameter of basal dendrites of layer II/III pyramidal neurons [two-way ANOVA: F(1,29) = 0.0012, p = 0.973). (E) Total spine density is increased in CIE mice at 7 days withdrawal but not at 0 day withdrawal [0 day WD: F(1,4) = 0.22, p = 0.66; 7 day WD: F(1,7) = 8.59, *p < 0.05].