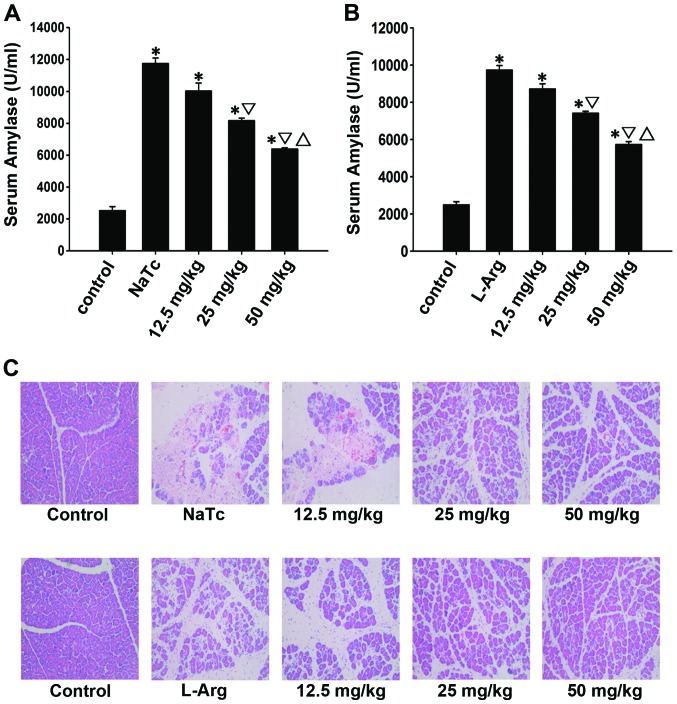
Figure 1.
Results of the prelilminary experiment. The activity of AS-IV on AP was evaluated based on (A and B) the serum amylase level and (C) pancreatic histological alterations. In rats with NaTc/L-Arg-induced AP, the serum amylase levels were significantly increased compared with those of the normal control group (P<0.05). However, pre-treatment with the high dose (50 mg/kg) of AS-IV led to a more effective decrease in the serum amylase level compared with moderate dose (25 mg/kg) and low dose (12.5 mg/kg). Morever, the high dose (50 mg/kg) of AS-IV markedly reduced interstitial edema, inflammatory cell infiltration and acinar cell necrosis. Data are represented as the means ± SD from 3 independent experiments. *P<0.05 compared with the normal control group at the same time point; ▽P<0.05 compared with the NaTc/L-Arg + vehicle-treated group at the same time point; △P<0.05 compared with the 25 mg/kg NaTc/L-Arg + AS-IV-treated group. AS-IV, astragaloside IV; NaTc, sodium taurocholate; L-Arg, L-arginine; AP, acute pancreatitis.