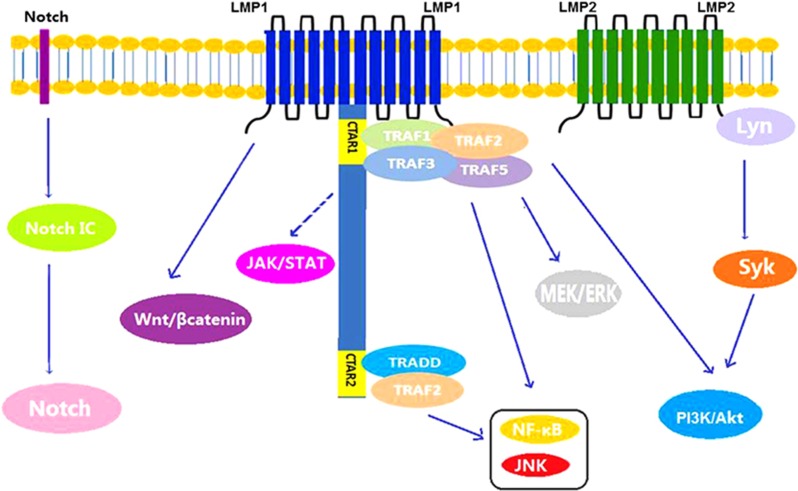
Figure 2.
Signaling pathways in T/NK-cell proliferation. NF-κB pathway in EBV-positive T-cell lymphoma: a diagrammatic depiction of the pathogenesis and molecular mechanisms associated with progression from hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) to chronic active disease or T-cell lymphoma in Epstein–Barr virus (EBV)-infected T cells. EBV latent membrane protein-1 (LMP-1) upregulates tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) via TNF receptor (TNFR) associated factors (TRAF)/nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signals on one hand to kill bystander lymphoid cells and downregulates TNFR-1 on the other hand to suppress the apoptotic signaling pathway, thus conferring survival from TNF-α-induced apoptosis on LMP-1-expressing T cells.