Figure 1. BRAT1 is a possible member of mTOR pathways and critical for cell growth.
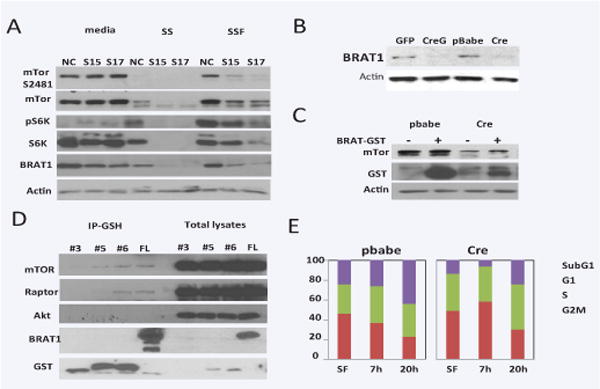
A. Control (NC) and BRAT1 knockdown (S15 and S17) Hela cells were cultured in 10% FBS/DMEM (media) or serum-free DMEM for 24 h (SS), followed by 10% complete DMEM for 2 h (SSF). Total lysates were isolated and subjected to immunoblotting with indicated antibodies. Actin was used as internal control to validate protein loading. B. Mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) were isolated from E15 of BRAT1flox/flox female mouse as described in Materials and Methods. Cells were transfected with GFP only (V) or Cre-GFP plasmid (CreG). C. Immortalized MEFs infected with pBabe retrovirus (pbabe) or Cre gene retrovirus (Cre) were transfected with BRAT-GST plasmid (+) or GST vector plasmid (−). After 48 hour, Total lysates were subjected to immunoblot. D. 293 cells were transfected with plasmids expressing GST-fusion fragments (#3, 5, 6) or full-length (FL) of BRAT1. Total lysates (1 mg/sample) were subjected to immunoprecipitation with GSH-sepharose beads. After immunoprecipitation, samples were blotted with the indicated antibodies. E. Control (pbabe) and BRAT1 knockout (Cre) MEFs were culture in plain DMEM for 24 hr, and then re-cultured in 10% complete DMEM for 7 or 20 h. Cell cycle was quantified by single-parameter flow cytometry after PI staining. Graphs represent percentages of cells in sub-G1, G1, S, and G2/M phases. Data shown here are representative of three independent experiments performed.
