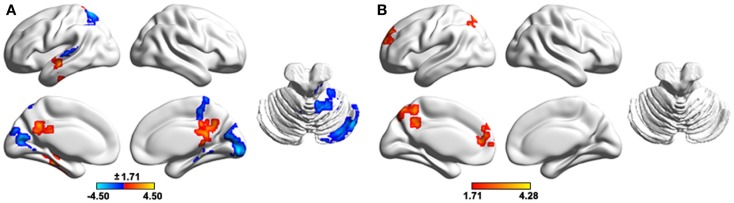
Figure 7.
The effects of regional gray matter volume on the functional results of weighted degree centrality. (A), Spatial correlation between regional gray matter volume and weighted degree centrality. (B), Between- group differences in weighted degree centrality after controlling for regional gray matter volume. The results were obtained in one general linear model, with weighted degree centrality as the dependent variable, group status (0 or 1) and voxel-specific gray matter volume as independent variables, and gender, age, and head motion as unconcerned covariates. The results were mapped into the brain surface using the BrainNet viewer (http://www.nitrc.org/projects/bnv/).