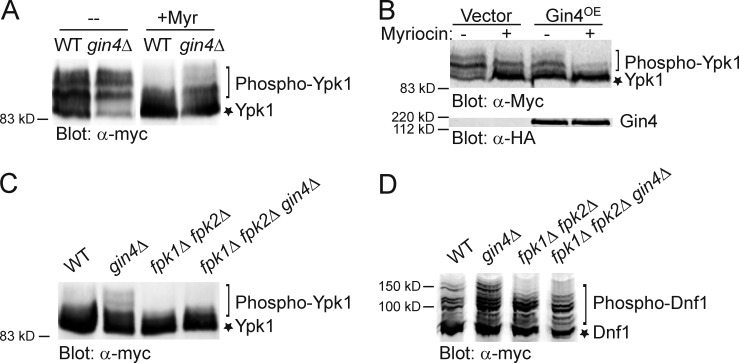
Figure 1.
Gin4 negatively regulates Fpk1-dependent phosphorylation of Ypk1 and Dnf1. (A) Wild-type (WT) strain (BY4741) or an isogenic gin4Δ mutant (YAT100) expressing Ypk1-myc from the GAL1 promoter (pAM76) were grown to mid-exponential phase, then either mock-treated or treated with Myr (1.25 µM) as indicated, collected, and lysed. The resulting extracts were resolved by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by immunoblotting with anti–c-myc mAb 9E10. (B) As in A, except that wild-type cells (Y258) carried both a plasmid expressing Ypk1-myc from the GAL1 promoter (pAM54) and either an empty vector (BG1805) or the same vector expressing Gin4 (pGin4-zz) from the GAL1 promoter. Gin4-zz was detected via its zz tag using an anti-HA mAb as a source of IgG. (C) As in A, except that a wild-type strain (BY4741) or isogenic gin4Δ mutant (YAT100), fpk1Δ fpk2Δ double mutant (YFR205), or fpk1Δ fpk2Δ gin4Δ triple mutant (YFR278) were used and only the Myr-treated cells are shown. (D) Same as in C, except that the cells expressed Dnf1(1403–1571)-myc from plasmid pES10 and the extract was analyzed using a Phos-tag gel.