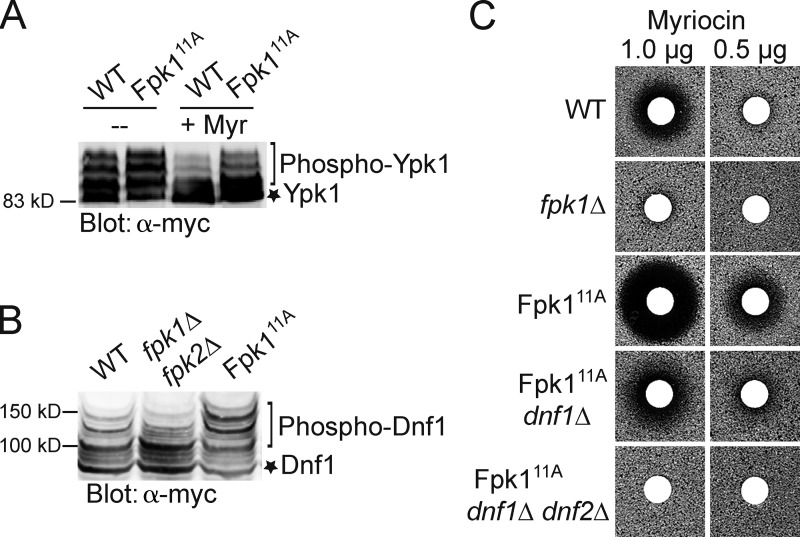
Figure 3.
Phosphorylation by Gin4 down-regulates Fpk1 activity. (A) Cells expressing either wild-type Fpk1 (BY4741, WT) or Fpk111A (YJW2) and also expressing Ypk1-myc from the GAL1 promoter (pAM76) were grown to mid-exponential phase, untreated or treated with Myr (1.25 μM), and lysed. The resulting extracts were resolved by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by immunoblotting with anti–c–myc mAb 9E10. (B) Cells expressing wild-type Fpk1 (BY4741, WT), an isogenic strain lacking both Fpk1 and Fpk2 (YFR205, fpk1Δ fpk2Δ) or expressing Fpk111A (YJW2) and also expressing Dnf1(1403–1571)–myc from the GAL1 promoter (pES10) were grown to mid–exponential phase and lysed. The resulting extracts were resolved on a Phos-tag gel and analyzed by immunoblotting with anti–c–myc mAb 9E10. (C) Wild-type (BY4742, WT), fpk1Δ (JTY6581), Fpk111A (YFR307), Fpk111A dnf1Δ (YFR308), or Fpk111A dnf1Δ dnf2Δ (YFR312) strains, as indicated, were plated as a lawn on YPD plates and then overlaid immediately at the center with a sterile filter paper disk onto which a solution containing the indicated amounts of Myr had been spotted. After incubation at 30°C for 2 d, plates were photographed.