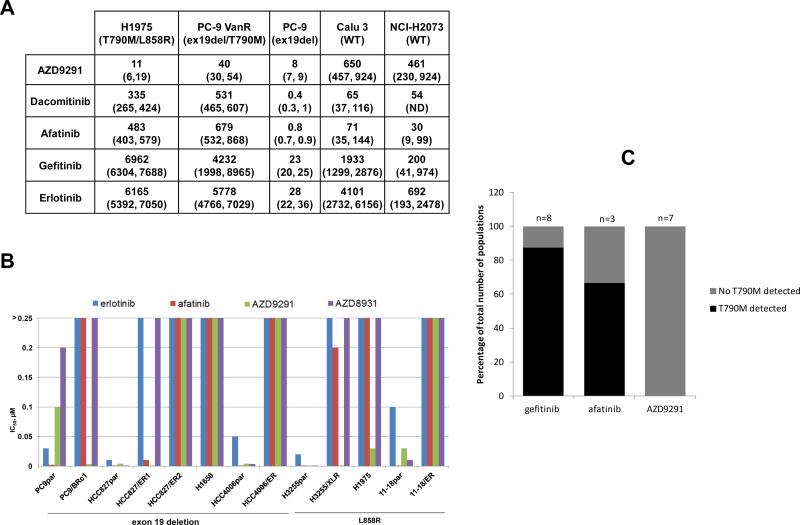
Figure 3.
Additional characteristics of AZD9291 in vitro. A, AZD9291 demonstrates greater inhibition of viability against mutant EGFR cell lines compared to wild-type, as assessed using a Sytox Green live/dead assay measured after 3 days treatment. The data represents the geomean IC50 nM value from at least two separate experiments (expressed with 95% confidence intervals where n>3). B, Sensitivity of isogenic pairs of EGFR mutant drug-sensitive and –resistant lung cancer cell lines (PC-9, ex19del; PC-9/BRc1, ex19del/T790M; HCC827, ex19del; HCC827/ER1, ex19del/T790M; HCC827/ER2, ex19del/METamplification; H1650, ex19del/PTEN loss; HCC4006, ex19del; HCC4006/ER, EMT (epithelial mesenchymal transition); H3255, L858R; H3255/XLR, L858R/T790M; H1975, L858R/T790M; 11-18, L858R; 11-18/ER, L858R/NRAS) to AZD9291, erlotinib, and afatinib. IC50s (μM) were based on data obtained from growth inhibition assays. C, T790M mutation was detected in multiple independent populations of PC-9 cells with acquired resistance to gefitinib or afatinib, but not in populations resistant to AZD9291.