Figure 4.
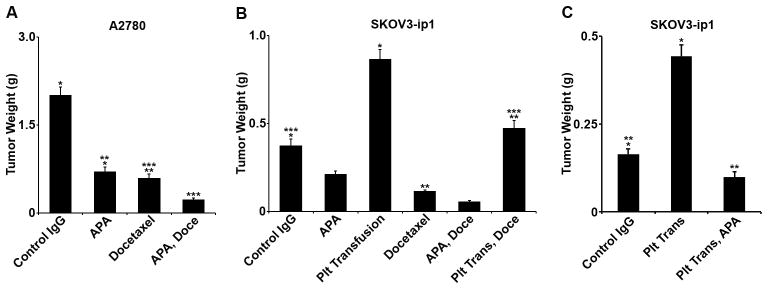
A. In vivo, A2780-bearing nude mice were treated with a control IgG, a platelet-depleting IgG anti-platelet antibody (APA), docetaxel, or a combination of the docetaxel and APA. Animals treated with APA had a 65% decrease in mean aggregate tumor weight compared to control (p = 0.008) that was similar to the 70% decrease that resulted from treatment with docetaxel (p = 0.004 compared to control). There was no statistical difference between the APA treatment and docetaxel treatment (p = 0.35). Mice treated with both the APA and docetaxel had an additional 62% reduction in aggregate tumor weight compared to that achieved by docetaxel alone (p = 0.04).
B. In vivo, SKOV3-ip1-bearing nude mice were treated with control IgG, APA, and docetaxel, and/or platelet transfusion. Platelet depletion with APA resulted in a 43% decrease in mean aggregate tumor weight of borderline significance (p = 0.07). Docetaxel resulted in a similar reduction in mean aggregate tumor weight (69%, p = 0.006). Mice given platelet transfusions had a 2.4-fold increase in mean aggregate tumor weight compared to control (p = 0.01). Compared to mice treated with docetaxel, mice treated with docetaxel and platelet transfusion had a 4-fold increase in mean aggregate tumor weight (p = 0.004). Mice given platelet transfusions and treated with docetaxel had a similar mean aggregate tumor weight to that of untreated controls (p = 0.55). Compared to mice treated with docetaxel, mice treated with APA and docetaxel had a 51% decrease in mean tumor weight (p = 0.02).
C. In vivo, SKOV3-ip1-bearming nude mice were treated with control IgG, platelet transfusion, or platelet transfusion with APA. Platelet transfusion resulted in a 70% increase in mean aggregate tumor weight (p = 0.001) whereas the combination of platelet transfusion with APA resulted in a non-significant 40% decrease in mean aggregate tumor weight compared to control (p = 0.06).
