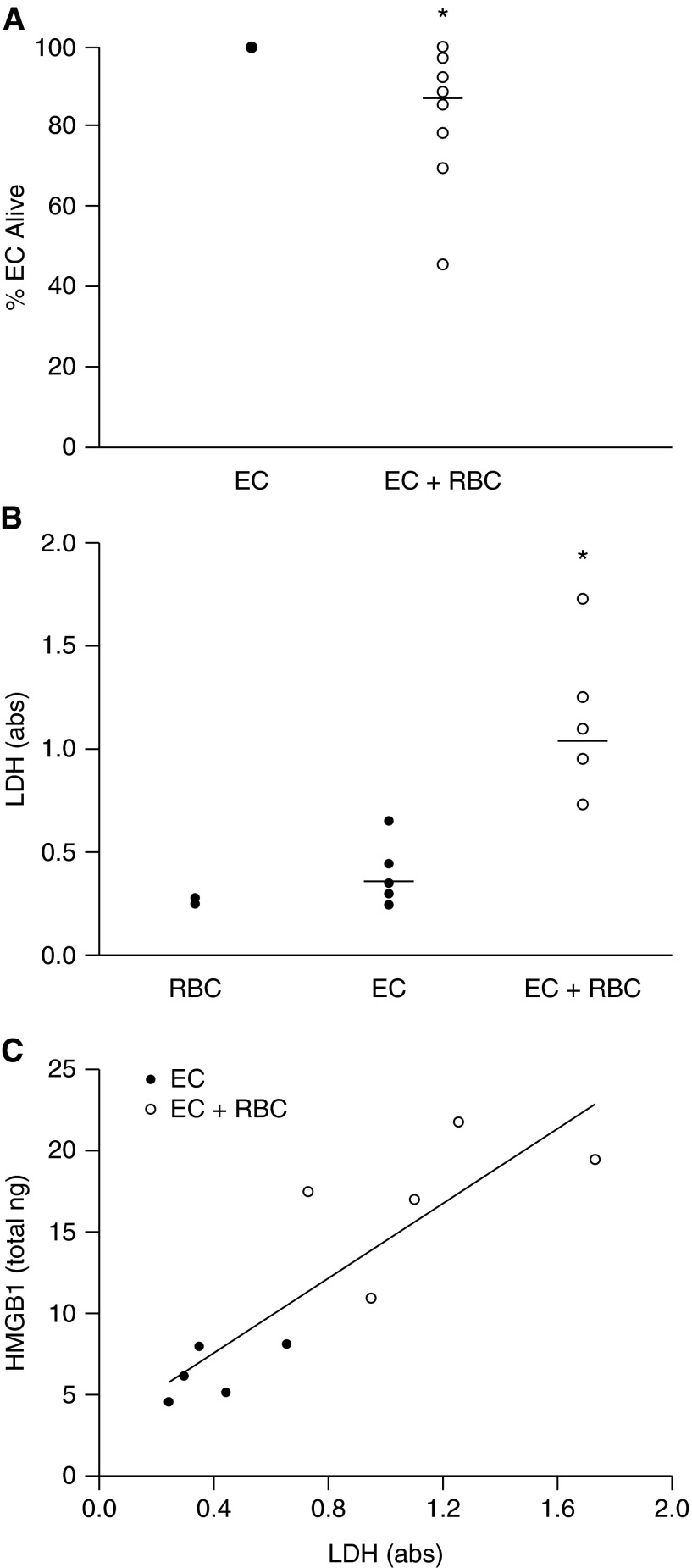
Figure 2.
Red blood cells (RBCs) induce lung endothelial cell (EC) death. (A) Following stimulation with RBCs, there is decreased recovery of lung EC, *P = 0.009. Eleven RBC units tested. Each open circle represents a different RBC unit, data representative of four independent studies. (B) RBC treatment increases lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release, *P < 0.01. (C) Correlation between high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) release and LDH, Spearman rank sum correlation coefficient = 0.92, P < 0.001.