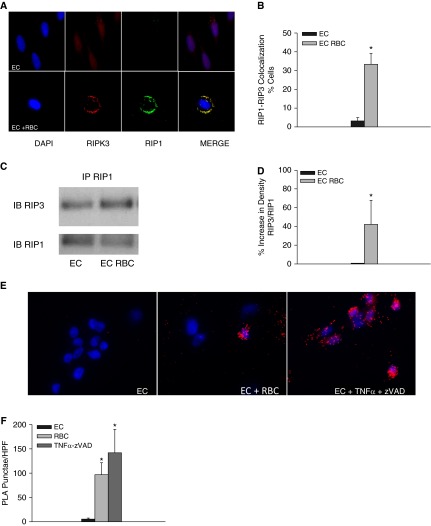
Figure 3.
Red blood cells (RBCs) induce formation of the necrosome complex in lung endothelial cells (ECs). (A) receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 1 (RIP1) and RIP3 in naive and RBC-treated human lung microvascular ECs (HMVEC-L). (B) Quantification of colocalization, P = 0.015. (C) Detection of RIP1 and RIP3 containing complexes by immunoprecipitation. (D) Densitometery of RIP1-RIP3 complexes, P < 0.01. Data represent four independent studies, five RBC units tested, one representative RBC unit depicted in Figure 5C. (E) Proximity ligation assay for RIP1 and RIP3 in naive and RBC-treated HMVEC-L, cells treated with tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and ZVAD are depicted in the rightmost panel. (F) Quantification of PLA puncta, *P < 0.01 when compared with EC alone. PLA = proximity ligation assay.