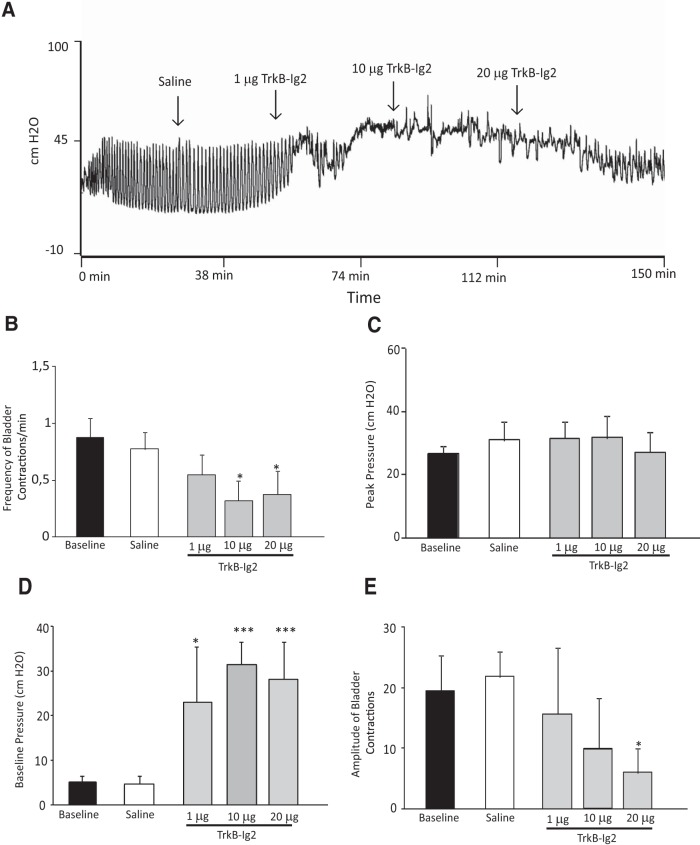
Figure 3.
A, Representative cystometrograms of 4 week SCI animals following acute intrathecal injection of saline and TrkB-Ig2 and parameter analysis of bladder function. A, Intrathecal administration of saline did not alter bladder function when compared with baseline. In contrast, intrathecal injection of TrkB-Ig2 dose dependently abolished bladder hyperactivity. Bar graphs depict the mean frequency (B), peak pressure (C), baseline pressure (D), and amplitude (E) of bladder contractions of 4 week SCI animals treated with either saline or 1 μg, and 10 and 20 μg of TrkB-Ig2. The frequency and amplitude of bladder contractions significantly decreased after intrathecal injection of 10 and 20 μg of TrkB-Ig2 (*p < 0.05 vs baseline values). No changes were found in peak pressure, but baseline pressure was markedly augmented after administration of 1, 10, and 20 μg of TrkB-Ig2 (***p < 0.001 vs baseline values).