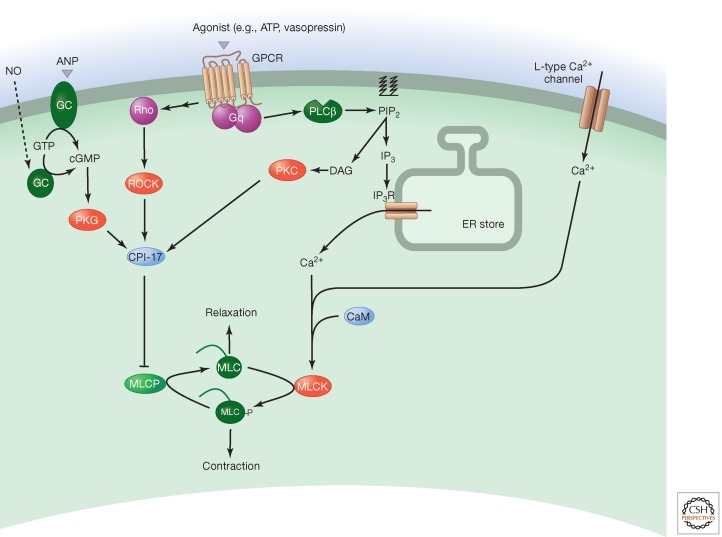
Figure 5.
Smooth muscle contraction. Calcium released by L-type calcium channels or IP3Rs downstream from Gq-coupled cell-surface receptors causes smooth muscle contraction. It binds to calmodulin (CaM) and the resulting complex stimulates myosin light-chain (MLC) kinase (MLCK). This phosphorylates MLC to promote contraction. A RhoA/ROCK pathway and a diacylglycerol (DAG) pathway contribute to calcium sensitization by altering the phosphorylation status of myosin light-chain phosphatase (MLCP). Relaxation is mediated through the cGMP/PKG pathway downstream from nitric oxide (NO) and agonists such as atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP).