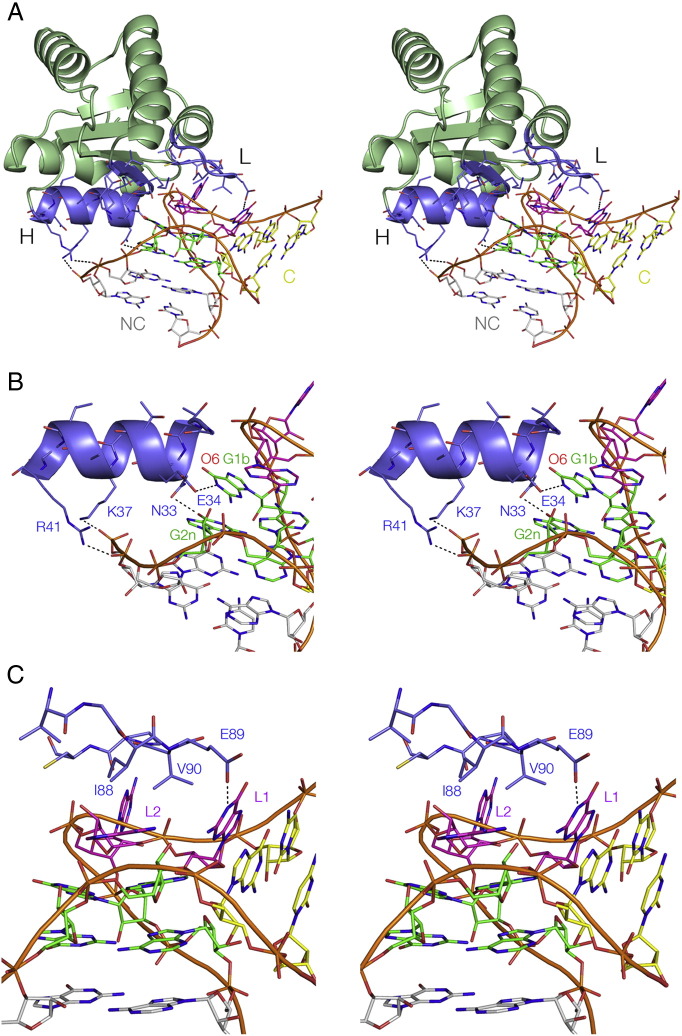
Fig. 9.
The structure of a complex between H. marismortui Kt-7 and A. fulgidus L7Ae complex, determined crystallographically at 2.3 Å resolution [39].
A. An overall view of the complex, showing the protein (depicted in cartoon form) bound in the major groove on the outer face of the K-turn. The two key regions of L7Ae involved in binding the RNA are highlighted in blue; these are the α-helix (H) and the hydrophobic loop (L).
B. The α-helix interacting with the major groove of the NC helix. R41 and K37 make non-specific interactions with the backbone, while E34 and N33 make specific hydrogen bonds to the conserved guanine nucleobases G1b and G2n respectively. The electronegative O6 atom of G1b is placed at the positive pole of the helix dipole of the α-helix.
C. The hydrophobic loop capping the loop region of the K-turn. The loop sits over the L2 and L1 nucleobases, with I88 and V90 on the lower face contributing to a large hydrophobic contact area. The carboxylate sidechain of E89 is hydrogen bonded to GL1 N1.