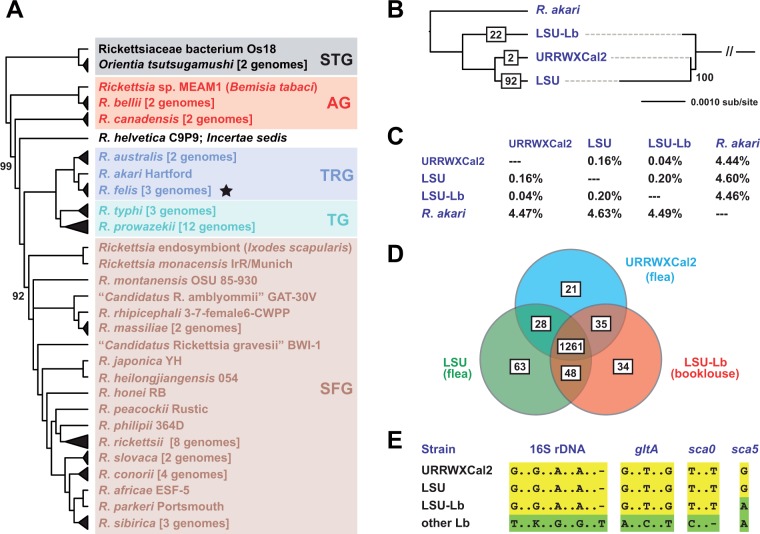
Fig. 1.—
Comparative analysis of R. felis genomes. (A) Genome-based phylogeny estimated for 62 Rickettsiaceae taxa. A total of 310 core proteins, encoded only once in all genomes, were utilized for OG generation, OG alignment (and masking of less conserved positions), and concatenation of aligned OGs (see text). Phylogeny of the final data set (56,920 aa) was estimated using the CAT–GTR model of substitution as implemented in PhyloBayes v3.3 (Lartillot and Philippe 2004, 2006). Tree is a consensus of 3,813 trees (discarding burn-in of 1,000 trees) pooled from two independent Markov chains run in parallel. Branch support (100%, or provided otherwise) was measured through posterior probabilities, which reflect frequencies of clades among the pooled trees. The R. felis clade is noted with a star. Rickettsiaceae classification scheme follows previous studies (Gillespie et al. 2007; Gillespie, Nordberg, et al. 2012; Driscoll et al. 2013). Complete taxon names, PATRIC genome IDs (Gillespie et al. 2011; Wattam et al. 2014), and genome statistics are provided in supplementary table S2, Supplementary Material online. (B) Phylogeny estimated from a second alignment of the abovementioned 310 core proteins, exclusive to the three R. felis genomes and R. akari (221,668 aa). Cladogram at left shows the branching pattern with unique positions in boxes. Phylogram at right shows the branch lengths for the three R. felis lineages. (C) Approximation of R. felis genome divergence. Calculated % divergence (116 informative aa sites from 310 core proteins) with DIVEIN (Deng et al. 2010), using the WAG (top) and Blosum62 (bottom) amino acid substitution models. Rickettsia akari str. Hartford was used as the outgroup. (D) Distribution of OGs generated across R. felis genomes. A further description of the breakdown of all input proteins from each genome, as well as results from manual evaluation, is provided in supplementary figure S2, Supplementary Material online. (E) Comparison of R. felis strains URRWXCal2, LSU, and LSU-Lb with other strains of R. felis identified from booklice. Yellow, SNPs uniting R. felis str. LSU-Lb with strains URRWXCal2 and LSU; green, SNPs uniting R. felis str. LSU-Lb with other booklouse-associated strains. Full alignments illustrating the positions of SNPs are provided in supplementary figure S4, Supplementary Material online.